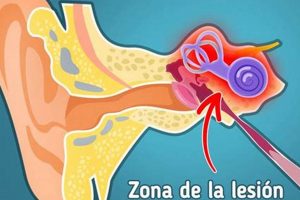
The sensation of ringing, buzzing, or humming in the left ear, experienced without an external sound source, is a common phenomenon. This auditory perception, often referred to medically as tinnitus, can manifest in various ways and range in intensity. The experience is subjective, meaning only the individual affected can perceive it.
Understanding the potential causes behind this auditory experience is crucial for proper management and relief. It can stem from a variety of factors, including exposure to loud noises, ear infections, wax buildup, certain medications, or underlying health conditions such as Meniere’s disease or temporomandibular joint (TMJ) disorders. Historically, such auditory anomalies were often attributed to supernatural or mystical causes before medical understanding advanced.
The following sections will delve into the specific potential causes, diagnostic approaches, and management strategies for addressing this type of auditory sensation, offering a comprehensive overview of the factors involved and potential avenues for relief.
Addressing Auditory Sensations in the Left Ear
Individuals experiencing persistent or concerning auditory sensations in the left ear may find the following tips helpful in navigating the potential causes and management strategies.
Tip 1: Monitor the Sensation: Pay close attention to the characteristics of the perceived sound. Note the pitch, intensity, and duration of the sensation, as well as any associated symptoms such as dizziness or hearing loss. Detailed observation can aid in diagnosis.
Tip 2: Review Medication List: Certain medications, including some antibiotics, anti-inflammatory drugs, and antidepressants, are known to be ototoxic, potentially causing or exacerbating auditory sensitivities. Consult a physician or pharmacist to determine if any current medications could be contributing.
Tip 3: Evaluate Noise Exposure: Prolonged or intense exposure to loud noises is a common cause. Limit exposure to such environments and consistently utilize hearing protection when unavoidable. Construction workers, musicians, and individuals attending loud concerts are particularly at risk.
Tip 4: Manage Stress and Anxiety: Stress and anxiety can exacerbate the perception of auditory sensations. Incorporate stress-reducing techniques such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, or yoga into the daily routine. Cognitive behavioral therapy can also be beneficial.
Tip 5: Address Underlying Medical Conditions: Auditory sensations can be a symptom of underlying medical conditions, such as Meniere’s disease, temporomandibular joint (TMJ) disorders, or cardiovascular issues. Seek medical evaluation to rule out or manage these conditions.
Tip 6: Consider Cerumen Management: Impacted earwax (cerumen) can cause various auditory disturbances. Consult a healthcare professional for safe and effective earwax removal. Avoid using cotton swabs, as they can push wax further into the ear canal.
Tip 7: Maintain a Healthy Lifestyle: A balanced diet, regular exercise, and adequate sleep can contribute to overall ear health. Avoid excessive consumption of caffeine, alcohol, and nicotine, as these substances can potentially worsen auditory symptoms.
Consistently implementing these strategies, along with seeking professional medical advice, can significantly improve the management of auditory sensitivities in the left ear and contribute to improved quality of life.
These tips provide a foundation for understanding and addressing the various factors that can contribute to auditory experiences. The subsequent section will provide detailed insights on potential diagnostic approaches and treatment options.
1. Tinnitus
The phenomenon commonly described as “que significa cuando zumba el oido izquierdo” often manifests as tinnitus. Tinnitus, by definition, is a subjective auditory perception; it is the experience of sound in the absence of an external acoustic stimulus. This inherent subjectivity is a crucial element in understanding, diagnosing, and managing the condition.
- Individual Variability
The perception of tinnitus varies significantly among individuals. The sound’s characteristics its pitch, loudness, and nature (e.g., ringing, buzzing, hissing) are unique to each person. This variability necessitates individualized assessment and treatment strategies because what one person describes as a high-pitched ringing, another may experience as a low-frequency hum.
- Emotional and Psychological Impact
The subjective nature extends beyond the sound itself to the emotional and psychological response it elicits. For some, tinnitus is a minor annoyance, while for others, it can lead to significant distress, anxiety, depression, and sleep disturbances. The degree of impact is highly individual and is influenced by factors such as coping mechanisms, pre-existing mental health conditions, and the perceived control over the sensation.
- Diagnostic Challenges
The subjectivity of tinnitus presents challenges in diagnosis. Since there is no objective measure of the sound itself, diagnosis relies heavily on the patient’s self-report. This necessitates careful and detailed history taking, as well as ruling out other potential causes of the auditory sensation, such as physical abnormalities or underlying medical conditions, via physical examinations and audiological testing.
- Treatment Personalization
Due to its subjective nature and varied impact, treatment for tinnitus must be highly personalized. There is no single cure for tinnitus, and management strategies often involve a combination of approaches, including sound therapy, cognitive behavioral therapy, tinnitus retraining therapy, and medication to address associated anxiety or depression. The specific approach is tailored to the individual’s unique experience and needs.
The core understanding that tinnitus is a subjective experience is paramount to appropriately responding to the question, “que significa cuando zumba el oido izquierdo.” It emphasizes the importance of individualized care, comprehensive assessment, and a multifaceted approach to managing this often-complex condition. Recognition of this subjectivity prevents a one-size-fits-all approach and promotes targeted interventions designed to improve the individual’s quality of life.
2. Underlying cause identification
The auditory sensation, often described as “que significa cuando zumba el oido izquierdo,” necessitates a thorough investigation to identify potential underlying causes. This step is paramount because the perceived sensation is often a symptom of an underlying medical condition or environmental factor. Identifying the root cause enables targeted interventions and management strategies rather than merely addressing the symptom itself.
Several potential causes contribute to such auditory experiences. These range from relatively benign conditions like earwax buildup or minor ear infections to more serious disorders such as Meniere’s disease, acoustic neuromas, or cardiovascular issues. Exposure to ototoxic medications or loud noises can also be significant contributing factors. A comprehensive medical history, physical examination, and audiological testing are essential tools in discerning the specific cause. For instance, an individual experiencing the described auditory sensation might undergo an audiogram to assess hearing function, or imaging studies like MRI to rule out structural abnormalities. Without proper identification, treatments may be ineffective or even detrimental. If the auditory issue resulted from ototoxic medication the only way to stop that is by stop taking that kind of mediciens.
Ultimately, the successful resolution or management of this auditory sensation depends on accurately pinpointing the underlying cause. A failure to identify and address the root problem can lead to chronic symptoms, reduced quality of life, and potentially the progression of undiagnosed medical conditions. Therefore, prompt and thorough medical evaluation is crucial when experiencing unexplained auditory phenomena.
3. Hearing loss association
The auditory experience described as “que significa cuando zumba el oido izquierdo” frequently exhibits a strong association with hearing loss. While not universally present, the occurrence of tinnitus alongside diminished auditory acuity is statistically significant and merits careful evaluation. This connection suggests shared underlying mechanisms affecting the auditory pathway.
The presence of hearing loss can affect or result to auditory experience. For example, a patient experiencing both hearing loss and tinnitus could have sensorineural damage affecting both hearing and nerve function, causing auditory sensations. A detailed audiological evaluation, including audiometry and speech discrimination testing, provides essential data in determining the degree and type of hearing loss, thus guiding diagnostic and management strategies. Ignoring the hearing loss association when evaluating the causes of auditory sensation could lead to incomplete diagnosis. An audiologist might consider the degree of hearing loss when proposing tinnitus treatments, such as hearing aids to compensate for auditory deficits and potentially reduce tinnitus perception.
The association between hearing loss and the described auditory phenomenon underscores the importance of comprehensive audiological assessment in individuals experiencing these symptoms. Identifying and addressing any underlying hearing loss can significantly improve management strategies and enhance overall patient outcomes. Recognizing this connection is critical for clinicians and patients alike in navigating the complexities of auditory health.
4. Vascular contributions analysis
Vascular contributions analysis, in relation to “que significa cuando zumba el oido izquierdo,” involves a careful examination of how blood flow and vascular health might influence the experience of auditory sensations. This analysis is crucial because disturbances in the circulatory system can manifest as auditory symptoms, potentially impacting the ear’s function or the auditory pathways in the brain.
- Pulsatile Tinnitus Assessment
Pulsatile tinnitus, a rhythmic sound often described as a whooshing or throbbing in sync with the heartbeat, is a key indicator of potential vascular involvement. Analyzing the characteristics of the sound, its correlation with the pulse rate, and any positional changes affecting the sound’s intensity helps identify vascular anomalies such as arteriovenous malformations, carotid artery stenosis, or venous sinus stenosis. For example, a patient reporting pulsatile tinnitus that changes with head position might undergo imaging studies to assess the vascular structures near the ear.
- Blood Pressure Evaluation
Elevated blood pressure, or hypertension, can contribute to the development or exacerbation of tinnitus. High blood pressure can increase the force of blood flow through the vessels of the inner ear, potentially leading to damage or dysfunction. Regular monitoring of blood pressure, along with lifestyle modifications or pharmacological interventions to manage hypertension, can play a significant role in alleviating related auditory symptoms. Furthermore, hypotensive episodes may cause auditory disturbances through reduced blood flow to the auditory system.
- Vascular Imaging Techniques
When vascular contributions are suspected, imaging techniques such as magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) and computed tomography angiography (CTA) become invaluable diagnostic tools. These imaging modalities allow for detailed visualization of the blood vessels surrounding the ear and brain, enabling the detection of structural abnormalities, aneurysms, or blockages that could be causing the auditory sensations. For example, MRA can help identify a vascular loop pressing on the auditory nerve, a rare but treatable cause of tinnitus.
- Impact of Atherosclerosis
Atherosclerosis, the buildup of plaque in the arteries, can reduce blood flow to the inner ear and brain, potentially leading to auditory dysfunction. Evaluation for atherosclerosis, especially in individuals with risk factors such as smoking, diabetes, or hyperlipidemia, is an important aspect of vascular contributions analysis. Lifestyle modifications, medication, or even surgical interventions to improve blood flow may be necessary to address the underlying vascular disease and alleviate associated auditory symptoms.
In summary, the analysis of vascular contributions is a critical component in understanding “que significa cuando zumba el oido izquierdo.” By considering factors such as pulsatile tinnitus, blood pressure, vascular imaging, and atherosclerosis, clinicians can more effectively diagnose and manage auditory sensations arising from vascular abnormalities. This comprehensive approach ensures that underlying vascular issues are addressed, potentially improving auditory health and overall well-being.
5. Neurological impact scrutiny
Neurological impact scrutiny is essential when assessing “que significa cuando zumba el oido izquierdo” due to the auditory system’s intricate connection with the central nervous system. Auditory sensations, particularly those arising without external stimuli, can indicate underlying neurological conditions affecting auditory pathways or brain function.
- Auditory Nerve Assessment
The auditory nerve, or vestibulocochlear nerve (CN VIII), plays a pivotal role in transmitting auditory information from the inner ear to the brainstem. Scrutinizing its function through auditory brainstem response (ABR) testing or imaging studies is crucial. Neurological conditions such as acoustic neuromas, which are benign tumors on the auditory nerve, can cause tinnitus and hearing loss. ABR testing can reveal abnormalities in neural conduction time, while MRI can visualize the nerve and detect any structural anomalies. Thus, evaluation of the auditory nerve provides a key step to examine the effects that may lead to auditory sensation.
- Central Auditory Processing Evaluation
Central auditory processing refers to the brain’s ability to interpret and understand auditory information. Neurological disorders affecting the brainstem, auditory cortex, or related pathways can disrupt this processing, leading to tinnitus or other auditory distortions. Central auditory processing disorder (CAPD) testing can evaluate various auditory skills, such as sound localization, auditory discrimination, and temporal processing. Cognitive deficits or traumatic brain injuries that impact these regions of the brain can manifest as atypical auditory sensations.
- Neuromodulation Considerations
Neuromodulation techniques, such as transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) and transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS), are emerging as potential treatments for chronic tinnitus. These techniques aim to modulate neural activity in specific brain regions associated with tinnitus perception, such as the auditory cortex and dorsal lateral prefrontal cortex. Neurological impact scrutiny guides the application of neuromodulation by identifying the specific brain regions to target and monitoring the effects of stimulation on tinnitus symptoms.
- Vestibular System Interaction
The vestibular system, responsible for balance and spatial orientation, shares anatomical and functional connections with the auditory system. Neurological conditions affecting the vestibular system, such as vestibular neuritis or Mnire’s disease, can cause both vertigo and auditory symptoms, including tinnitus. Evaluating vestibular function through tests like videonystagmography (VNG) or caloric testing helps determine the extent of vestibular involvement and guide appropriate management strategies. This assessment is also important when one has “que significa cuando zumba el oido izquierdo”.
By thoroughly scrutinizing the neurological impact, medical professionals can better understand the underlying mechanisms contributing to “que significa cuando zumba el oido izquierdo” and develop targeted treatment plans. This comprehensive approach, integrating audiological and neurological assessments, aims to improve outcomes and enhance the quality of life for individuals experiencing persistent auditory sensations.
6. Lifestyle factor influence
Lifestyle factors exert a significant influence on the experience of auditory sensations described as “que significa cuando zumba el oido izquierdo.” These factors, encompassing dietary habits, physical activity, stress levels, and substance use, can directly or indirectly impact auditory health, predisposing individuals to, or exacerbating existing, auditory conditions. Prolonged exposure to loud noise within occupational or recreational settings, a prominent lifestyle consideration, is a well-documented etiological factor in noise-induced hearing loss and subsequent tinnitus. Similarly, dietary habits characterized by high sodium intake can contribute to fluid imbalances in the inner ear, potentially triggering or intensifying auditory symptoms.
Stress, a pervasive element of contemporary lifestyles, has been implicated in the modulation of tinnitus perception. Chronic stress and anxiety can activate the sympathetic nervous system, increasing the sensitivity of the auditory system and heightening the awareness of auditory sensations. Conversely, adopting stress-reduction techniques, such as mindfulness or regular exercise, may mitigate the perceived severity of tinnitus. Substance use, including excessive caffeine or alcohol consumption, can also disrupt inner ear homeostasis, altering auditory thresholds and promoting tinnitus. For example, individuals with pre-existing tinnitus may find their symptoms worsen following the consumption of caffeinated beverages or alcoholic drinks. Therefore, lifestyle adjustments aimed at minimizing noise exposure, moderating substance use, managing stress, and maintaining a balanced diet represent critical strategies for mitigating auditory symptoms.
In summary, lifestyle factors are inextricably linked to the manifestation and management of auditory sensations characterized as “que significa cuando zumba el oido izquierdo.” Understanding and modifying these factors can serve as a primary intervention strategy for preventing and alleviating such auditory disturbances. While lifestyle modifications may not eliminate all cases of tinnitus or related symptoms, they often contribute significantly to improving auditory health and overall quality of life. Further research is needed to elucidate the precise mechanisms through which specific lifestyle elements influence auditory perception and to develop tailored interventions for managing auditory symptoms.
Frequently Asked Questions
The following questions address common concerns regarding auditory sensations experienced in the left ear. The provided answers offer general information and do not constitute medical advice.
Question 1: Is an occasional auditory sensation in the left ear cause for immediate concern?
An isolated instance of ringing or buzzing in the left ear is typically not an emergency. However, persistent, worsening, or accompanied by other symptoms such as hearing loss, dizziness, or headache warrants prompt medical evaluation.
Question 2: What are the most common triggers for experiencing auditory sensations in one ear?
Common triggers include exposure to loud noises, earwax buildup, ear infections, certain medications, stress, and underlying medical conditions such as Meniere’s disease or temporomandibular joint (TMJ) disorders.
Question 3: Can the auditory sensation be a sign of a serious underlying medical condition?
In some instances, yes. While often benign, such sensations can indicate conditions like acoustic neuroma, cardiovascular issues, or neurological disorders. Thorough medical evaluation is crucial to rule out serious underlying causes.
Question 4: What types of medical professionals should be consulted for this type of auditory issue?
An audiologist is the primary specialist for hearing-related concerns. An otolaryngologist (ENT doctor) can assess the ear, nose, and throat. A neurologist may be consulted if neurological issues are suspected.
Question 5: Are there any self-care measures that can help alleviate the auditory sensation?
Potential self-care measures include avoiding loud noises, managing stress, ensuring proper ear hygiene (avoiding cotton swabs), and limiting caffeine and alcohol intake. If symptoms persist, professional medical advice is essential.
Question 6: Is there a definitive cure for this type of auditory sensation?
A definitive cure is not always possible, especially if the sensation is related to chronic conditions like tinnitus. However, various management strategies, including sound therapy, cognitive behavioral therapy, and medication, can effectively reduce the severity and impact of the sensation.
Prompt diagnosis and management are essential for addressing auditory sensations in the left ear, contributing to enhanced quality of life.
The following section will delve into strategies for the management of auditory issues.
Conclusion
The exploration of “que significa cuando zumba el oido izquierdo” reveals a complex interplay of potential factors, ranging from benign transient occurrences to indicators of underlying medical conditions. Careful assessment, encompassing audiological evaluations, vascular considerations, neurological scrutiny, and lifestyle analysis, is paramount for accurate diagnosis and management. The subjective nature of the auditory experience necessitates individualized approaches, recognizing that the etiology and impact vary significantly among individuals.
Addressing auditory sensations requires vigilance and proactive engagement with healthcare professionals. Continued research and technological advancements offer promise for improved diagnostic capabilities and treatment modalities, aiming to enhance the well-being of those affected by these auditory phenomena. Individuals experiencing persistent or concerning auditory symptoms are encouraged to seek prompt medical attention to facilitate timely intervention and optimize long-term auditory health.