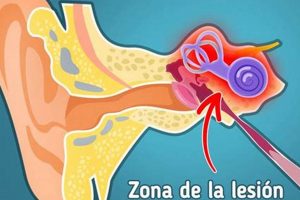
The sensation of ringing, buzzing, or hissing in the right ear is a common experience that can be attributed to a variety of causes. This auditory perception, occurring without an external sound source, is often referred to as tinnitus. The characteristics of this sound, as well as any accompanying symptoms, can provide clues to its underlying etiology. For example, the sound might be a high-pitched ringing, a low-frequency hum, or a complex mixture of tones.
Understanding the possible origins of this auditory phenomenon is essential for appropriate management. Potential causes range from benign and temporary conditions, such as exposure to loud noises or earwax buildup, to more complex medical issues involving the auditory system, cardiovascular system, or neurological system. The duration and intensity of the sound, as well as any associated symptoms like dizziness or hearing loss, are crucial factors in determining the appropriate course of action. A comprehensive evaluation by a healthcare professional is often necessary to identify the root cause and implement targeted interventions.
Further discussion will explore common causes, diagnostic approaches, and available treatment options for this condition, providing insights into managing and potentially alleviating the perceived sound. This includes a detailed examination of audiological testing, medical history review, and potential imaging studies to pinpoint the precise origin of the aural perception and guide individualized treatment strategies.
Addressing the perception of a buzzing or ringing sound in the right ear requires a strategic and informed approach. The following guidelines offer practical considerations for managing this experience.
Tip 1: Monitor Sound Exposure: Prolonged or intense exposure to loud noises is a frequent trigger for auditory disturbances. Employ hearing protection in noisy environments, such as concerts or workplaces with heavy machinery, to mitigate potential damage.
Tip 2: Review Medication Regimen: Certain medications are known to induce or exacerbate aural symptoms. Consult with a physician or pharmacist to evaluate potential ototoxic effects of current prescriptions and explore alternative options if warranted.
Tip 3: Manage Stress Levels: Elevated stress and anxiety can contribute to the perception of ringing in the ear. Implement stress-reduction techniques, such as mindfulness meditation or regular exercise, to promote overall well-being and potentially alleviate auditory symptoms.
Tip 4: Evaluate Dietary Habits: Excessive consumption of caffeine, alcohol, and sodium can affect blood flow and inner ear function, potentially triggering or intensifying aural sensations. Moderating intake of these substances may offer relief.
Tip 5: Address Underlying Medical Conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as hypertension, diabetes, and thyroid disorders, can be associated with auditory disturbances. Ensure appropriate management of these conditions through regular medical check-ups and adherence to prescribed treatments.
Tip 6: Maintain Cardiovascular Health: Good cardiovascular health is crucial for adequate blood circulation to the inner ear. Engage in regular physical activity, maintain a healthy diet, and monitor blood pressure to support auditory function.
Tip 7: Consult a Healthcare Professional: Persistent or severe auditory sensations warrant a thorough evaluation by an audiologist or otolaryngologist. Professional assessment can identify the underlying cause and guide appropriate treatment strategies.
Adopting these strategies can contribute to better management and potential reduction of perceived sound, leading to improved quality of life. However, professional medical advice remains paramount for accurate diagnosis and effective treatment.
The subsequent sections will delve into specific treatment modalities and long-term management strategies for individuals experiencing ongoing auditory disturbances.
1. Tinnitus
The subjective experience of que quiere decir cuando te zumba el oido derecho often aligns directly with the clinical understanding of tinnitus. Tinnitus encompasses a broad spectrum of perceived sounds, ranging from ringing and buzzing to hissing and clicking, all occurring without an external auditory stimulus. The interpretation and impact of this auditory perception varies significantly among individuals.
- Subjective Auditory Experience
Tinnitus, by definition, is a phantom auditory perception. The sensation, commonly experienced as ringing in the ear, stems from aberrant neural activity within the auditory pathways. This internal generation of sound underscores the subjective nature of tinnitus; only the affected individual can perceive it. Real-life examples include patients describing a high-pitched whine or a low-frequency hum. This subjective quality makes objective measurement challenging, relying heavily on patient self-reporting for diagnosis and assessment.
- Neural Correlates
The neural mechanisms underlying tinnitus are complex and not fully understood. Research suggests involvement of the auditory cortex, brainstem, and even non-auditory areas of the brain. The generation of phantom sounds may arise from altered neural plasticity, auditory deprivation, or imbalances in inhibitory and excitatory neurotransmission. Understanding these neural correlates is crucial for developing targeted therapeutic interventions, such as neuromodulation techniques.
- Psychological Impact
The persistent perception of sound can have significant psychological consequences, affecting an individual’s quality of life. Tinnitus can lead to annoyance, stress, anxiety, depression, and sleep disturbances. The psychological impact is often exacerbated by the inability to control or eliminate the perceived sound. Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) and tinnitus retraining therapy (TRT) are commonly employed to address the psychological distress associated with tinnitus, focusing on modifying negative thought patterns and promoting habituation to the sound.
- Variability in Perception
The way individuals perceive and react to tinnitus varies widely. Factors such as age, hearing loss, personality traits, and coping mechanisms influence the subjective experience. Some individuals may habituate to the sound and experience minimal distress, while others may find it debilitating. The characteristics of the perceived sound, such as its loudness, pitch, and tonal quality, also contribute to the overall impact. This variability highlights the importance of individualized assessment and management strategies.
Therefore, the expression que quiere decir cuando te zumba el oido derecho often mirrors the complex reality of tinnitus, encompassing both the sensory perception of sound and the multifaceted psychological and neurological factors that shape an individual’s experience. A comprehensive understanding of these elements is essential for effective diagnosis, management, and ultimately, improving the quality of life for those affected by this condition.
2. Possible Underlying Conditions
The occurrence of a ringing sensation in the right ear, which can be interpreted as ” que quiere decir cuando te zumba el oido derecho,” may signal the presence of various underlying medical conditions. These conditions range from localized ear disorders to systemic diseases impacting multiple organ systems. Identifying and addressing these potential root causes is critical for effective management and prevention of further complications. The auditory system’s sensitivity makes it susceptible to a wide range of physiological disturbances.
Specific examples of underlying conditions associated with aural perceptions include Meniere’s disease, characterized by episodic vertigo, hearing loss, and tinnitus; acoustic neuroma, a benign tumor affecting the auditory nerve; and otosclerosis, a condition involving abnormal bone growth in the middle ear. Cardiovascular issues such as hypertension and atherosclerosis can also contribute, as compromised blood flow to the inner ear can disrupt auditory function. Moreover, metabolic disorders, including diabetes and thyroid dysfunction, have been linked to auditory disturbances. Certain medications, due to their ototoxic properties, can also induce or exacerbate ” que quiere decir cuando te zumba el oido derecho.” For instance, prolonged use of high-dose aspirin or certain antibiotics can damage the delicate structures of the inner ear.
Therefore, a thorough medical evaluation is paramount when an individual experiences persistent or recurring ” que quiere decir cuando te zumba el oido derecho.” This evaluation should include a comprehensive medical history, physical examination, audiological testing, and potentially imaging studies to identify or rule out any underlying medical conditions. Timely diagnosis and appropriate management of these conditions can often alleviate or mitigate the auditory symptom and prevent further deterioration of auditory function. Recognizing this connection underscores the importance of considering ” que quiere decir cuando te zumba el oido derecho” not merely as a symptom, but as a potential indicator of a broader health issue requiring attention.
3. Auditory system examination.
An auditory system examination is crucial in determining the etiology of ” que quiere decir cuando te zumba el oido derecho.” This comprehensive assessment evaluates the structure and function of the ear, auditory nerve, and central auditory pathways to identify potential sources of the perceived auditory sensation.
- Otoscopic Examination
The initial step typically involves otoscopy, a visual inspection of the ear canal and tympanic membrane. This allows for the identification of obstructions such as cerumen impaction, foreign bodies, or signs of infection that may contribute to ” que quiere decir cuando te zumba el oido derecho.” For example, impacted earwax can cause pressure on the eardrum, leading to tinnitus. This examination is essential to rule out easily treatable causes.
- Audiometry
Audiometry is a fundamental hearing test that assesses the patient’s ability to detect sounds at various frequencies and intensities. This test can reveal the presence of hearing loss, which is a common correlate of ” que quiere decir cuando te zumba el oido derecho.” Certain patterns of hearing loss, such as those seen in noise-induced hearing loss or age-related hearing loss, are frequently associated with tinnitus. Audiometry also helps differentiate between conductive and sensorineural hearing loss, guiding further diagnostic evaluation.
- Tympanometry
Tympanometry measures the movement of the tympanic membrane in response to changes in air pressure. This test can identify middle ear dysfunction, such as fluid accumulation or eardrum perforation, which may contribute to ” que quiere decir cuando te zumba el oido derecho.” For example, patients with otitis media with effusion may experience tinnitus due to the altered pressure dynamics in the middle ear. Tympanometry aids in determining the integrity of the middle ear system.
- Otoacoustic Emissions (OAEs)
OAEs are sounds produced by the outer hair cells of the cochlea in response to auditory stimulation. Measuring OAEs can provide information about the function of the cochlea, the inner ear structure responsible for converting sound vibrations into electrical signals. Reduced or absent OAEs may indicate cochlear damage, which is often associated with ” que quiere decir cuando te zumba el oido derecho.” This test is particularly useful in identifying subtle cochlear dysfunction that may not be detected by standard audiometry.
The findings from an auditory system examination provide valuable insights into the potential causes of ” que quiere decir cuando te zumba el oido derecho.” By systematically evaluating the various components of the auditory system, clinicians can develop a targeted management plan to address the underlying issues contributing to the auditory perception and improve the patient’s quality of life.
4. Cardiovascular health impact.
The phrase ” que quiere decir cuando te zumba el oido derecho” can be associated with various cardiovascular conditions. The auditory system’s function is critically dependent on adequate blood flow. Compromised cardiovascular health, such as hypertension, atherosclerosis, or other circulatory disorders, can disrupt this blood supply, potentially leading to ischemia or damage to the delicate structures of the inner ear. The cochlea, in particular, relies on a consistent and sufficient blood supply for optimal function, and any reduction in blood flow can manifest as tinnitus, or the perception of ringing in the ear. Real-life examples include individuals with uncontrolled hypertension reporting a pulsatile tinnitus, where the perceived sound synchronizes with their heartbeat, reflecting changes in blood pressure. Additionally, individuals with atherosclerosis may experience tinnitus due to reduced blood flow to the inner ear caused by narrowed or blocked arteries.
Further, the interplay between cardiovascular risk factors and auditory health is significant. Conditions like hyperlipidemia, diabetes, and smoking can contribute to both cardiovascular disease and auditory dysfunction. For instance, smoking damages blood vessels and reduces oxygen delivery to the inner ear, increasing the risk of both cardiovascular events and tinnitus. Regular monitoring of cardiovascular health, including blood pressure, cholesterol levels, and glucose levels, is crucial for maintaining adequate auditory function. Lifestyle modifications, such as adopting a heart-healthy diet, engaging in regular exercise, and avoiding smoking, can positively impact both cardiovascular and auditory health. Addressing cardiovascular risk factors can potentially mitigate or prevent ” que quiere decir cuando te zumba el oido derecho” in some individuals.
In summary, the potential connection between cardiovascular health and ” que quiere decir cuando te zumba el oido derecho” highlights the importance of considering systemic health conditions in the evaluation of auditory symptoms. Identifying and managing cardiovascular risk factors can be a crucial component of a comprehensive approach to addressing tinnitus. While not all cases of tinnitus are directly attributable to cardiovascular issues, maintaining optimal cardiovascular health can contribute to overall auditory well-being and reduce the risk of various auditory disturbances.
5. Stress, diet, and medications.
Stress, diet, and medications represent interconnected factors that can significantly influence the perception of tinnitus, often expressed as ” que quiere decir cuando te zumba el oido derecho.” The interplay between these elements may either trigger or exacerbate the experience of ringing in the ear. Chronic stress, for instance, can activate the sympathetic nervous system, leading to increased blood pressure and altered blood flow to the inner ear, potentially inducing or intensifying tinnitus symptoms. Dietary factors, such as excessive consumption of caffeine, alcohol, or sodium, can also affect inner ear function and contribute to the onset or worsening of auditory perceptions. Similarly, certain medications possess ototoxic properties, meaning they can damage the inner ear and cause tinnitus as a side effect. Examples include high doses of aspirin, certain antibiotics, and some chemotherapy drugs. Understanding these connections is vital for effective management strategies, emphasizing the need for a holistic approach to address tinnitus.
Furthermore, the synergistic effects of these factors should not be overlooked. An individual experiencing chronic stress may turn to unhealthy dietary habits, such as consuming excessive caffeine or alcohol, to cope with stress. These behaviors, combined with the physiological effects of stress itself, can create a cascade of events that contribute to the manifestation of tinnitus. Similarly, individuals taking multiple medications may be at a higher risk for experiencing drug-induced tinnitus due to the cumulative ototoxic effects of different drugs. Identifying and mitigating these synergistic effects requires a comprehensive evaluation of an individual’s lifestyle, medical history, and medication regimen. Practical applications involve implementing stress-reduction techniques, such as mindfulness meditation or yoga, adopting a balanced diet low in sodium and caffeine, and carefully reviewing medications with a healthcare provider to identify potential ototoxic agents and explore alternative options when available.
In conclusion, stress, diet, and medications exert considerable influence on the perception of ” que quiere decir cuando te zumba el oido derecho.” Managing these factors through lifestyle modifications, dietary changes, and medication adjustments represents a crucial component of a comprehensive approach to tinnitus management. While addressing these elements may not completely eliminate tinnitus in all cases, it can contribute to a significant reduction in symptom severity and an improvement in overall quality of life. The challenge lies in the complexity of these interactions and the need for individualized strategies tailored to each person’s specific circumstances. Linking this understanding to broader themes of health and wellness underscores the importance of proactive self-care and informed decision-making in managing tinnitus and promoting overall auditory health.
Frequently Asked Questions
This section addresses common inquiries regarding the sensation of ringing or buzzing in the right ear (often described as ” que quiere decir cuando te zumba el oido derecho“), providing factual information and guidance.
Question 1: What factors might induce ” que quiere decir cuando te zumba el oido derecho“?
Numerous factors can contribute to this auditory perception. Common causes include exposure to loud noises, earwax buildup, certain medications, underlying medical conditions (such as Meniere’s disease or cardiovascular issues), stress, and dietary factors such as excessive caffeine or sodium intake. A thorough medical evaluation is often necessary to pinpoint the specific cause.
Question 2: Is ” que quiere decir cuando te zumba el oido derecho” always indicative of a serious medical condition?
Not necessarily. In many instances, the sensation is temporary and benign, resolving on its own or with simple interventions like earwax removal. However, persistent or recurring episodes, particularly when accompanied by other symptoms such as hearing loss, dizziness, or headache, warrant further investigation by a healthcare professional to rule out more serious underlying conditions.
Question 3: How is ” que quiere decir cuando te zumba el oido derecho” typically diagnosed?
Diagnosis usually involves a comprehensive medical history, physical examination, and audiological testing. The examination may include otoscopy (visual inspection of the ear canal), audiometry (hearing test), tympanometry (assessment of middle ear function), and potentially imaging studies such as MRI or CT scans to evaluate the auditory pathways and rule out structural abnormalities.
Question 4: What treatment options exist for ” que quiere decir cuando te zumba el oido derecho“?
Treatment strategies depend on the underlying cause. If earwax buildup is the culprit, removal can provide relief. For medication-induced tinnitus, adjusting or discontinuing the offending drug may be necessary. In cases of underlying medical conditions, treating the condition itself often alleviates the tinnitus. Other approaches include sound therapy, tinnitus retraining therapy (TRT), cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT), and the use of hearing aids to mask the perceived sound.
Question 5: Can lifestyle modifications help manage ” que quiere decir cuando te zumba el oido derecho“?
Yes, certain lifestyle modifications can be beneficial. These include protecting ears from loud noises, managing stress levels through relaxation techniques, limiting caffeine and alcohol intake, maintaining a healthy diet, and addressing underlying cardiovascular risk factors such as high blood pressure or cholesterol.
Question 6: When should a medical professional be consulted regarding ” que quiere decir cuando te zumba el oido derecho“?
Consultation with a healthcare professional is recommended if the tinnitus is persistent, bothersome, accompanied by other symptoms (such as hearing loss, dizziness, or headache), or significantly impacting quality of life. Early evaluation can facilitate accurate diagnosis and appropriate management.
In summary, the sensation of ringing in the right ear, or ” que quiere decir cuando te zumba el oido derecho,” is a complex symptom with a variety of potential causes. A thorough medical evaluation and appropriate management strategies are essential for addressing this issue.
The following section explores strategies for long-term management and coping with persistent auditory sensations.
Understanding Ringing in the Right Ear
This exploration of ” que quiere decir cuando te zumba el oido derecho” has highlighted the diverse origins and potential implications of this auditory experience. It is established that such a sensation can stem from a variety of factors, ranging from benign and transient causes to indicators of underlying medical conditions. Effective management necessitates a comprehensive evaluation, encompassing audiological assessments, medical history review, and consideration of lifestyle influences such as stress, diet, and medication use. Individualized treatment strategies, guided by accurate diagnosis, are paramount for mitigating the impact on an individual’s well-being.
Given the potential for this symptom to reflect broader health concerns, proactive engagement with medical professionals is encouraged. Ongoing research continues to refine our understanding of the auditory system and develop targeted interventions. Seeking timely and informed care remains crucial for optimizing auditory health and improving the quality of life for those affected by ” que quiere decir cuando te zumba el oido derecho.”