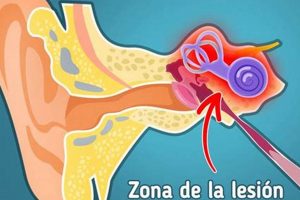
The sensation of experiencing ringing, buzzing, or hissing sounds in the right ear, even in the absence of external auditory stimuli, is a common auditory perception. This unilateral manifestation can vary in intensity and duration, and its presence may be intermittent or constant.
Understanding the potential underlying causes and appropriate management strategies is crucial. Addressing this auditory phenomenon can significantly improve an individual’s quality of life by reducing distress and facilitating better communication. Investigations into the history of auditory perception offer insights into its diverse manifestations and potential correlations with various health conditions.
The following sections will explore the potential causes, diagnostic approaches, and available treatments for this specific auditory experience. Further discussion will cover methods for coping with the sensation and strategies to prevent its occurrence.
Management Strategies for Right Ear Tinnitus
The following guidelines offer potential avenues for managing the perception of sounds in the right ear, absent of external sources. These strategies are designed to provide general guidance and should not be considered substitutes for professional medical advice.
Tip 1: Seek Professional Evaluation: An audiologist or otolaryngologist can conduct comprehensive hearing tests and assess the underlying cause of the auditory perception. Identifying the root cause is essential for effective management.
Tip 2: Explore Sound Therapy Options: White noise machines, masking devices, or customized soundscapes can help reduce the perceived intensity of the internal sounds. Experiment with different sound frequencies and amplitudes to find optimal relief.
Tip 3: Manage Stress Levels: Stress can exacerbate the perception of internal auditory stimuli. Incorporate relaxation techniques such as deep breathing exercises, meditation, or yoga into daily routines.
Tip 4: Review Medication Regimen: Certain medications can contribute to auditory disturbances. Consult with a healthcare provider to review current medications and explore potential alternatives, if applicable.
Tip 5: Minimize Exposure to Loud Noises: Protection from loud sounds is crucial to prevent further auditory damage. Wear earplugs or earmuffs in noisy environments.
Tip 6: Address Underlying Medical Conditions: Manage any underlying medical conditions, such as high blood pressure, diabetes, or temporomandibular joint (TMJ) disorders, as these can sometimes contribute to auditory disturbances.
Tip 7: Consider Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): CBT can assist in managing the emotional distress and negative thoughts associated with persistent auditory perceptions. A trained therapist can provide strategies for coping with the sensation.
Adherence to these strategies may contribute to a reduction in the perceived intensity and impact of the auditory experience. It is important to maintain open communication with healthcare professionals throughout the management process.
The subsequent sections will delve into specific treatment modalities and further explore the relationship between lifestyle factors and the perception of these internal sounds.
1. Auditory Perception
Auditory perception, the process by which the brain interprets sound, is central to understanding the sensation described as a buzzing or ringing in the right ear. This phenomenon, occurring in the absence of external sound sources, indicates a misfiring or aberrant signal within the auditory system. The auditory cortex, responsible for sound processing, receives input from the inner ear via the auditory nerve. Disruptions along this pathway, whether originating in the cochlea, auditory nerve, or even within the brain itself, can lead to the perception of phantom sounds. For instance, damage to hair cells in the cochlea, often resulting from noise exposure, can lead to spontaneous neural activity that the brain interprets as sound. Similarly, certain neurological conditions can alter auditory processing, leading to the creation of auditory hallucinations.
The importance of auditory perception as a component lies in its role as the final interpreter of the auditory signal. Even if the initial transduction of sound waves in the ear is normal, if the brain misinterprets or generates its own signals, the individual experiences the sensation. This underscores the complexity of the auditory system and highlights that the issue may not always be with the ear itself. Consider, for example, individuals with phantom limb syndrome who experience sensations in a limb that is no longer present. This illustrates the brain’s capacity to create sensations independently of external stimuli, a principle that extends to auditory perception as well. Consequently, identifying and addressing auditory perception abnormalities is critical in managing this kind of issue.
In summary, a comprehensive understanding of auditory perception is vital for diagnosing and managing phantom auditory sensations. The challenges lie in pinpointing the exact location and cause of the disrupted neural signals. However, by focusing on auditory processing within the brain, medical professionals can develop targeted interventions aimed at modulating neural activity and alleviating the sensation, emphasizing the role of understanding “me zumba el oido derecho.”
2. Right Ear Specificity
The unilateral presentation of auditory sensations, characterized by their localization to the right ear, introduces a layer of complexity to the exploration of this phenomenon. Consideration of right ear specificity is essential for differential diagnosis and targeted intervention.
- Anatomical Asymmetry
Subtle differences in the anatomical structure or physiological function of the right ear compared to the left may predispose it to certain types of auditory disturbances. While gross anatomical variations are rare, minute differences in cochlear morphology or neural pathways could contribute to unilateral susceptibility. For instance, variations in the diameter of the internal auditory canal could impact nerve compression and subsequent auditory symptoms.
- Lateralized Exposure to Trauma
Physical trauma or acoustic injury affecting primarily the right side of the head or ear can lead to localized auditory damage. Examples include exposure to loud noises specifically directed toward the right ear, or head injuries sustained on the right side. Such incidents can result in damage to the cochlea, tympanic membrane, or ossicles, contributing to the development of unilateral auditory sensations. This is particularly relevant in occupational settings or recreational activities involving asymmetrical noise exposure.
- Vascular Variations
The vascular supply to the inner ear, specifically the labyrinthine artery, may exhibit variations that predispose the right ear to ischemia or vascular compromise. Reduced blood flow to the cochlea can lead to hair cell damage and the subsequent generation of phantom auditory signals. Atherosclerosis or other vascular abnormalities may preferentially affect the right labyrinthine artery, leading to right ear specificity. Consideration of vascular risk factors is therefore important in the evaluation.
- Neurological Lateralization
While auditory processing is generally bilateral, subtle differences in hemispheric dominance for certain auditory functions may influence the perception of unilateral sensations. Although not fully understood, variations in cortical representation of auditory information from each ear might contribute to the lateralized manifestation of this phenomenon. Further research into the neural correlates of unilateral auditory sensations is needed to fully elucidate this aspect.
In summary, the localization of auditory sensations to the right ear necessitates a comprehensive assessment that considers anatomical, traumatic, vascular, and neurological factors. Understanding these potential right ear-specific etiologies is crucial for accurate diagnosis and the development of targeted management strategies, emphasizing the nuances associated with “me zumba el oido derecho”.
3. Subjective Experience
The sensation commonly referred to as a buzzing or ringing in the right ear represents a profoundly subjective experience. Its characteristics, intensity, and perceived impact vary significantly from individual to individual. The absence of objective, externally verifiable stimuli underscores the reliance on self-reporting and personal interpretation. Consequently, understanding the nuances of the subjective experience is paramount in clinical assessment and management.
The subjective nature of this phenomenon affects both diagnosis and treatment. Diagnostic protocols rely heavily on detailed patient histories, including descriptions of the sound’s quality (e.g., buzzing, hissing, ringing), its perceived location within the ear, its temporal pattern (constant vs. intermittent), and any associated symptoms (e.g., vertigo, hearing loss). Furthermore, the individual’s emotional and cognitive response to the sensation influences its overall impact. For example, one person might experience mild annoyance, while another might suffer from significant anxiety, depression, or sleep disturbance. Effective management strategies must therefore be tailored to address not only the perceived sound itself but also the associated psychological and emotional distress. Real-world examples include cases where individuals report complete resolution of auditory symptoms following counseling and stress reduction techniques, even in the absence of objective changes in auditory function. This highlights the powerful influence of subjective factors on symptom perception and management.
In summary, the subjective experience forms the cornerstone of understanding and addressing the sensation of a buzzing or ringing in the right ear. Recognizing the variability in symptom presentation, emotional response, and perceived impact is essential for developing individualized treatment plans. Overlooking the subjective component can lead to ineffective interventions and persistent patient distress. Addressing this necessitates a holistic approach incorporating audiological assessment, psychological support, and patient education, leading to improved outcomes and enhanced quality of life.
4. Potential Etiologies
The perception of internal auditory sensations, specifically when localized to the right ear, is often indicative of underlying etiologies that warrant careful consideration. Understanding the diverse range of potential causes is critical for guiding diagnostic investigations and tailoring appropriate management strategies. Several factors can contribute to the genesis of these subjective auditory experiences, spanning from peripheral auditory dysfunction to central nervous system involvement. Peripheral causes include damage to the cochlea, such as noise-induced hearing loss, age-related hearing loss (presbycusis), or ototoxic medication exposure. For instance, individuals with a history of prolonged exposure to loud noise without adequate hearing protection may develop hair cell damage in the cochlea, leading to the perception of ringing or buzzing sounds. Central causes involve abnormalities in the auditory pathways or cortex, potentially arising from neurological conditions, traumatic brain injury, or even psychological factors such as stress and anxiety. The clinical significance of recognizing these potential etiologies lies in the ability to differentiate between treatable and non-treatable causes, and to implement interventions that target the underlying pathology whenever possible.
Beyond the more common auditory and neurological factors, systemic conditions can also manifest as auditory disturbances. Vascular disorders, such as hypertension or atherosclerosis, can compromise blood flow to the inner ear, leading to ischemic damage and subsequent auditory symptoms. Metabolic disorders, such as diabetes or thyroid dysfunction, can also affect auditory function through various mechanisms. Moreover, temporomandibular joint (TMJ) disorders and cervical spine issues can indirectly contribute to auditory sensations due to their proximity to the ear and their potential to affect nerve function and muscle tension. Real-world examples include individuals with untreated hypertension experiencing pulsatile sensations in their ears, or patients with TMJ dysfunction reporting a clicking or popping sound in conjunction with their internal auditory perceptions. The importance of considering these systemic factors underscores the need for a comprehensive medical history and physical examination in evaluating individuals presenting with subjective auditory phenomena. Identifying and addressing these underlying systemic conditions can often lead to significant improvement in auditory symptoms, thereby enhancing the overall quality of life.
In summary, the relationship between potential etiologies and the sensation commonly described as a buzzing or ringing in the right ear is multifaceted and complex. Accurate identification of the underlying cause is paramount for effective management. Challenges include the subjective nature of the symptoms, the wide range of potential contributing factors, and the potential for multiple co-existing etiologies. However, a thorough evaluation that considers both auditory and non-auditory factors, coupled with appropriate diagnostic testing, can often reveal the root cause and guide targeted interventions. By recognizing the diverse range of potential etiologies and their impact on auditory perception, clinicians can improve diagnostic accuracy, optimize treatment strategies, and ultimately enhance the well-being of individuals experiencing this auditory phenomenon.
5. Impact on Well-being
The subjective auditory sensation, often described as a buzzing or ringing in the right ear, can have a profound impact on an individual’s overall well-being. This connection is multifaceted, extending beyond mere auditory annoyance to encompass psychological, cognitive, and social dimensions. The persistent nature of the auditory perception can lead to significant distress, particularly when it interferes with daily activities, sleep patterns, and concentration abilities. The inability to escape the internal sound can induce anxiety, frustration, and a sense of isolation, negatively affecting mood and emotional stability. Real-world examples include individuals who report difficulty focusing at work, impaired communication in social settings, and chronic fatigue due to sleep disturbances caused by the constant auditory perception. These experiences highlight the significance of addressing the impact on well-being as an integral component of managing this sensation.
The link between the auditory experience and psychological well-being is further substantiated by research demonstrating increased rates of depression and anxiety disorders among individuals experiencing chronic, persistent auditory sensations. The cognitive impact manifests as difficulty concentrating, impaired memory recall, and reduced attention span. This cognitive interference can hinder academic performance, professional productivity, and the ability to engage in everyday tasks. Socially, individuals may withdraw from social interactions due to difficulty hearing in noisy environments or the fear of discussing their condition with others. This social isolation can further exacerbate feelings of loneliness and depression, creating a negative feedback loop. The practical significance of understanding these interconnected effects lies in the recognition that effective management requires a holistic approach that addresses not only the auditory symptom itself, but also the associated psychological, cognitive, and social consequences.
In summary, the impact on well-being is a critical consideration in the context of experiencing the described auditory sensation. The challenges lie in accurately quantifying the subjective distress and tailoring interventions to address the diverse needs of affected individuals. Recognizing the multifaceted nature of this connection encompassing psychological, cognitive, and social domains is essential for developing comprehensive management strategies that improve overall quality of life. The ultimate goal is not only to reduce the auditory symptom but also to restore psychological equilibrium, enhance cognitive function, and facilitate meaningful social engagement, thereby mitigating the negative impact on well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions About Right Ear Auditory Sensations
The following questions address common inquiries regarding the perception of buzzing or ringing in the right ear, providing factual information to enhance understanding.
Question 1: What are the most common causes of “me zumba el oido derecho”?
The origins are varied, encompassing inner ear damage from noise exposure, age-related hearing changes, medication side effects, temporomandibular joint (TMJ) disorders, and, in some instances, neurological conditions affecting the auditory pathways.
Question 2: Is “me zumba el oido derecho” a sign of a serious underlying medical condition?
While not always indicative of a serious condition, persistent or sudden-onset auditory sensations warrant medical evaluation. They may signify underlying issues such as hearing loss, vascular problems, or neurological disorders that require diagnosis and management.
Question 3: Can stress or anxiety trigger “me zumba el oido derecho”?
Elevated stress levels and anxiety can exacerbate the perception of auditory sensations. Psychological stress can influence neural activity in the brain, potentially amplifying or triggering the sensation. Management of stress and anxiety can contribute to a reduction in symptom severity.
Question 4: What diagnostic tests are typically performed to investigate “me zumba el oido derecho”?
A comprehensive audiological evaluation, including pure-tone audiometry and tympanometry, is standard. Depending on the clinical presentation, additional tests may include imaging studies (MRI or CT scan) to rule out structural abnormalities and blood tests to assess for underlying medical conditions.
Question 5: Are there effective treatment options available for “me zumba el oido derecho”?
Management strategies vary depending on the underlying cause. Options may include sound therapy (e.g., white noise machines), hearing aids for associated hearing loss, medication for underlying medical conditions, cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) for managing distress, and lifestyle modifications to reduce stress and noise exposure.
Question 6: Can “me zumba el oido derecho” lead to permanent hearing loss?
The perception of sounds in the ear does not directly cause hearing loss. However, if the underlying cause is related to damage to the inner ear, this could contribute to hearing loss progression. Medical consultation is necessary for diagnosis and management.
The key takeaway is that experiencing this sensation requires medical evaluation to determine the root cause and implement appropriate management strategies to alleviate discomfort and prevent potential complications.
The subsequent section will explore practical coping mechanisms and preventative measures for managing right ear auditory perceptions.
Conclusion
The preceding exploration of the phenomenon encompassing right ear auditory sensations, frequently described as “me zumba el oido derecho,” elucidates a complex interplay of auditory perception, localized anatomical factors, subjective experience, potential etiologies, and consequential impacts on well-being. Comprehension of these interconnected elements is fundamental for effective diagnosis and management.
Given the multifaceted nature of this condition and its potential to signify underlying medical issues, individuals experiencing persistent or concerning symptoms are advised to seek professional medical evaluation. Early identification and intervention remain paramount for mitigating potential long-term effects and optimizing individual quality of life. Further research into the mechanisms underlying auditory processing and perception will undoubtedly contribute to enhanced diagnostic capabilities and more targeted therapeutic interventions.