Tinnitus, the perception of sound when no external noise is present, can manifest as a ringing, buzzing, hissing, or humming sensation. When experienced predominantly in the right ear, individuals often seek understanding of potential causes and associated meanings. Perceptions regarding its significance vary across cultures and personal beliefs, ranging from physiological explanations to interpretations rooted in folklore.
Understanding the potential origins of this unilateral auditory phenomenon is crucial for appropriate management. From a medical perspective, factors such as exposure to loud noises, ear infections, Meniere’s disease, and certain medications can contribute to its onset. Psychological factors like stress and anxiety can also exacerbate the perception of sound. Furthermore, some traditions and belief systems assign symbolic interpretations to physical sensations, linking them to spiritual or emotional states.
Investigating the potential underlying causes requires a multifaceted approach. Medical evaluation by an audiologist or physician is recommended to rule out any physical or neurological conditions. Concurrently, exploring coping mechanisms for managing the perceived sound, such as sound therapy or relaxation techniques, can improve quality of life. Alternative interpretations should be regarded with a critical and informed perspective.
Considerations for Unilateral Tinnitus
Addressing tinnitus experienced predominantly in the right ear necessitates a strategic and informed approach, encompassing medical evaluation, lifestyle adjustments, and informed decision-making.
Tip 1: Seek Professional Audiological Evaluation: A comprehensive hearing assessment by a qualified audiologist is crucial. This evaluation identifies potential underlying causes, such as hearing loss, ear infections, or other audiological conditions that may be contributing to the tinnitus.
Tip 2: Review Medication Regimen: Certain medications are known to have ototoxic effects, potentially triggering or exacerbating tinnitus. Consultation with a physician to review current medications and explore alternative options, if appropriate, is advisable.
Tip 3: Manage Noise Exposure: Prolonged exposure to loud noises can damage hearing and contribute to tinnitus. Implementing strategies to minimize noise exposure, such as wearing earplugs in noisy environments and limiting time spent in loud settings, is beneficial.
Tip 4: Implement Stress Reduction Techniques: Stress and anxiety can worsen tinnitus symptoms. Engaging in stress-reducing activities such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises may provide relief.
Tip 5: Explore Sound Therapy Options: Sound therapy involves using external sounds to mask or habituate to tinnitus. White noise machines, nature sounds, or specialized tinnitus masking devices can be utilized to reduce the perceived loudness and intrusiveness of the tinnitus.
Tip 6: Maintain a Healthy Lifestyle: A balanced diet, regular exercise, and adequate sleep contribute to overall well-being and can positively influence tinnitus perception. Avoiding excessive caffeine and alcohol consumption is also recommended.
Adherence to these recommendations can contribute to improved management of tinnitus focused in the right ear, fostering enhanced well-being and quality of life.
These strategies, while potentially helpful, should be considered in conjunction with professional medical advice to tailor a comprehensive management plan.
1. Medical Etiology
The term “si te zumba el oido derecho que significa,” translated as “if your right ear is ringing, what does it mean,” directly relates to medical etiology through the investigation of potential physical causes underlying the auditory perception. A core aspect of addressing right-sided tinnitus involves a thorough medical assessment to identify any physiological factors contributing to the symptom. Conditions such as Meniere’s disease, acoustic neuroma, temporomandibular joint (TMJ) disorders, or even simple earwax impaction can manifest as unilateral tinnitus. Therefore, the initial inquiry into the meaning of right ear ringing necessitates a focus on ruling out or identifying any underlying medical conditions requiring specific treatment.
The importance of medical etiology in the context of right-sided tinnitus stems from the potential for targeted intervention. For instance, if TMJ dysfunction is identified, dental or physical therapy may alleviate the tinnitus. Similarly, diagnosing and treating an ear infection can resolve the associated ringing. Identifying an acoustic neuroma, though rare, necessitates immediate attention due to its potential impact on hearing and neurological function. Failure to consider medical etiology can result in missed opportunities for effective treatment and potential progression of underlying conditions.
Consequently, the practical significance of understanding the connection between the symptom and its potential medical origins is paramount. A comprehensive medical evaluation, including audiological testing and possibly imaging studies, is essential to determine the root cause of the right ear ringing. This approach allows for informed decisions regarding treatment options and management strategies, ensuring that interventions are tailored to address the specific underlying cause rather than solely focusing on symptomatic relief.
2. Auditory Pathway
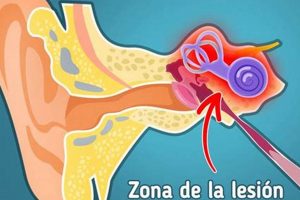
The auditory pathway, encompassing the intricate network of structures from the outer ear to the auditory cortex in the brain, plays a critical role in understanding the phenomenon described by “si te zumba el oido derecho que significa.” This phrase, referring to ringing in the right ear, often originates from disruptions or anomalies within this pathway. Damage to hair cells in the cochlea, lesions along the auditory nerve, or even irregularities in the brain’s processing centers can manifest as tinnitus localized to one ear. Therefore, exploring the integrity and functionality of the auditory pathway is essential in diagnosing the root cause of right-sided tinnitus.
Understanding the specific location of dysfunction within the auditory pathway allows for more targeted interventions. For example, if damage to the cochlea is identified through audiometry, strategies such as hearing aids or sound therapy may be employed to compensate for the auditory deficit and alleviate the perceived ringing. In cases where the auditory nerve is implicated, further neurological evaluation is warranted to rule out conditions like acoustic neuroma. Moreover, central auditory processing disorders can also contribute to tinnitus, necessitating specialized rehabilitative approaches. Mapping the precise location of the abnormality within the auditory pathway is thus paramount for effective management.
In summary, the auditory pathway forms the anatomical and physiological basis for understanding right ear ringing. Investigating its functionality, from the peripheral structures to the central auditory cortex, is crucial for identifying the underlying cause of the symptom. Accurate diagnosis of the source of the tinnitus along this pathway allows for the implementation of targeted therapies aimed at alleviating the ringing and improving the individual’s overall auditory experience. A comprehensive understanding of the auditory pathway is therefore fundamental in addressing the concerns expressed by “si te zumba el oido derecho que significa.”
3. Subjective Perception
The interpretation of “si te zumba el oido derecho que significa,” or “if your right ear is ringing, what does it mean,” is fundamentally intertwined with subjective perception. The auditory sensation of tinnitus, often described as ringing, buzzing, or hissing, exists solely within the individual’s awareness. Its presence, intensity, and associated distress are all filtered through the individual’s unique sensory processing and cognitive appraisal. Two individuals with the same underlying audiological condition may experience drastically different levels of tinnitus-related impact due to variations in their subjective perception.
The significance of subjective perception extends beyond the mere recognition of the sound. Factors such as emotional state, attention, and pre-existing beliefs can significantly influence how the tinnitus is experienced. For example, an individual experiencing high levels of stress may perceive the tinnitus as louder and more intrusive than when in a relaxed state. Similarly, individuals who attribute negative connotations to the ringing, perhaps associating it with illness or impending doom, may experience greater anxiety and distress. Coping mechanisms, such as sound therapy or cognitive behavioral techniques, aim to modify subjective perception by altering the individual’s response to the tinnitus rather than directly eliminating the sound itself. The effectiveness of these interventions highlights the crucial role of subjective experience in the overall impact of tinnitus.
In summary, the “meaning” derived from “si te zumba el oido derecho que significa” is highly individualized and contingent upon subjective perception. The same auditory stimulus can evoke vastly different responses depending on the individual’s emotional state, cognitive interpretation, and coping strategies. Understanding and addressing the subjective aspects of tinnitus is therefore paramount in developing effective management strategies that prioritize the individual’s unique experience and promote improved quality of life. The challenge lies in accurately assessing and addressing these subjective elements, necessitating a holistic and patient-centered approach to tinnitus management.
4. Neurological Factors
Neurological factors represent a crucial aspect in understanding the experience of “si te zumba el oido derecho que significa,” the sensation of ringing in the right ear and its associated implications. This symptom can frequently be traced back to neurological dysfunctions or variations within the auditory pathways and brain structures responsible for sound processing. The following facets highlight key neurological components relevant to this phenomenon.
- Auditory Cortex Activity
The auditory cortex, located in the temporal lobe of the brain, is responsible for processing auditory information. Aberrant activity within this region, such as increased spontaneous firing of neurons, can be perceived as tinnitus. Studies using neuroimaging techniques like fMRI have shown altered activity patterns in the auditory cortex of individuals experiencing chronic tinnitus. This hyperactivity may arise from deafferentation, where reduced auditory input from the ear leads to compensatory changes in cortical excitability. In the context of right ear ringing, localized dysfunction or imbalance in the right auditory cortex may be implicated.
- Neural Synchrony and Plasticity
The synchronized firing of neurons within the auditory pathway is essential for accurate sound perception. Disruptions in neural synchrony, potentially caused by noise-induced hearing loss or other neurological insults, can lead to the perception of tinnitus. Furthermore, the brain’s capacity for plasticity, its ability to reorganize neural connections, can contribute to the chronicity of tinnitus. Maladaptive plasticity, where the brain rewires itself in response to hearing loss, can lead to the persistent generation of phantom auditory signals. This is vital when exploring right ear ringing since it highlights how localized auditory damage could trigger broader neurological changes that reinforce unilateral tinnitus.
- Neurotransmitter Imbalances
Neurotransmitters, chemical messengers that transmit signals between neurons, play a critical role in auditory processing and the modulation of tinnitus. Imbalances in neurotransmitter systems, such as the glutamatergic and GABAergic systems, have been implicated in the pathophysiology of tinnitus. Excessive glutamate activity, an excitatory neurotransmitter, can lead to neuronal hyperexcitability and contribute to the perception of tinnitus. Conversely, reduced GABA activity, an inhibitory neurotransmitter, can diminish the brain’s ability to suppress unwanted auditory signals. Understanding these neurotransmitter dynamics is crucial for pharmacological interventions aimed at reducing tinnitus symptoms. For example, specific pharmaceutical studies has shown decreased gaba levels in individuals suffering from tinnitus.
- Central Auditory Processing
Central auditory processing refers to the brain’s ability to analyze and interpret auditory information. Deficits in central auditory processing can manifest as difficulties in sound localization, discrimination, and pattern recognition, potentially contributing to the perception of tinnitus. Lesions or dysfunctions in brainstem nuclei, thalamic relays, or cortical regions involved in auditory processing can disrupt the normal flow of auditory information and lead to the generation of phantom sounds. The neurological components responsible for central auditory processing may explain tinnitus in the absence of peripheral hearing loss.
The neurological facets described provide a framework for understanding how the brain can generate the sensation of “si te zumba el oido derecho que significa” in the absence of external sound. Considering these neurological factors is essential for a comprehensive assessment and management of tinnitus, particularly when peripheral causes have been ruled out. Further research into the neurological mechanisms underlying tinnitus is crucial for developing targeted and effective treatments for this often debilitating condition.
5. Psychological Impact
The perception of “si te zumba el oido derecho que significa,” or ringing in the right ear, extends beyond the physical sensation to encompass significant psychological ramifications. This auditory phenomenon, often persistent and intrusive, can trigger a cascade of emotional and cognitive responses that profoundly affect an individual’s well-being. Understanding these psychological dimensions is crucial for comprehensive management.
- Anxiety and Irritability
Persistent tinnitus, especially when localized to one ear, frequently induces anxiety and irritability. The constant awareness of the sound can be distressing, leading to heightened vigilance and difficulty relaxing. This state of heightened arousal can impair concentration, disrupt sleep patterns, and increase overall stress levels. The anxiety may manifest as apprehension about the tinnitus worsening, fear of underlying medical conditions, or frustration with the inability to escape the perceived sound.
- Depression and Low Mood
Chronic tinnitus can contribute to the development of depression and a persistent low mood. The relentless nature of the symptom, combined with its potential impact on sleep and daily functioning, can erode an individual’s sense of control and lead to feelings of hopelessness. Social isolation may exacerbate these feelings, as individuals may withdraw from activities and relationships due to the intrusiveness of the tinnitus. The psychological burden can significantly diminish quality of life and necessitate professional mental health support.
- Cognitive Interference and Concentration Difficulties
Tinnitus can significantly interfere with cognitive processes, particularly concentration and attention. The constant internal sound competes for attentional resources, making it difficult to focus on tasks that require sustained concentration. This cognitive interference can impair performance at work or school, hinder the ability to engage in leisure activities, and disrupt daily routines. The cognitive burden can lead to feelings of frustration, inadequacy, and reduced productivity.
- Sleep Disturbance and Insomnia
Tinnitus frequently disrupts sleep patterns and contributes to insomnia. The perceived sound can be particularly noticeable in quiet environments, making it difficult to fall asleep or stay asleep. Sleep deprivation can exacerbate anxiety, depression, and cognitive difficulties, creating a vicious cycle of psychological distress. Chronic sleep disturbance can further impair immune function, increase susceptibility to illness, and diminish overall physical and mental health.
The psychological impact of “si te zumba el oido derecho que significa” is multifaceted and often underestimated. Addressing these psychological dimensions through therapeutic interventions such as cognitive behavioral therapy, tinnitus retraining therapy, or pharmacological management is essential for improving overall well-being and enhancing coping strategies. A holistic approach that integrates audiological and psychological care is crucial for effectively managing the complex interplay between the physical and emotional aspects of tinnitus.
6. Cultural Beliefs
Cultural beliefs significantly shape interpretations and responses to physical sensations, including the perception of ringing in the right ear, as denoted by “si te zumba el oido derecho que significa.” These beliefs, varying widely across different societies and communities, influence whether the symptom is attributed to physiological causes, supernatural forces, or other symbolic meanings.
- Supernatural Portents
In several cultures, physical sensations such as ringing in the ears are interpreted as omens or signs from the spiritual realm. The specific ear affected might carry particular significance, with the right ear often associated with positive messages or warnings related to the future. Individuals within these cultures might seek guidance from traditional healers or spiritual leaders to decipher the meaning of the ringing and determine appropriate courses of action to mitigate potential negative outcomes or capitalize on auspicious opportunities. Ignoring these perceived messages could lead to feelings of anxiety or unease.
- Communication from Deceased Relatives
Certain belief systems attribute ringing in the ears to attempts by deceased relatives to communicate with the living. The specific ear affected may indicate the nature of the message or the identity of the relative attempting contact. Individuals subscribing to this belief might engage in rituals or practices aimed at facilitating communication with the departed, such as prayer, meditation, or consulting with a medium. The sensation may be interpreted as a comforting sign of continued connection or a request for assistance with unfinished business.
- Whispers from the Unseen World
In some traditions, ringing in the ears is viewed as the auditory perception of whispers or sounds emanating from the unseen world, populated by spirits, deities, or other supernatural entities. The content of these perceived whispers may be interpreted as guidance, warnings, or simply ambient noise from another dimension. Individuals experiencing this sensation might seek protection from malevolent spirits or attempt to discern the meaning of the messages through divination or other esoteric practices. The right ear may be associated with messages of a more benevolent or significant nature.
- Reflection of Energetic Imbalance
Within certain holistic and traditional medicine systems, ringing in the ears can be interpreted as a manifestation of energetic imbalances within the body. These imbalances may be attributed to disruptions in the flow of vital energy or blockages in specific energy pathways. The affected ear may correspond to particular organs or meridians, providing clues as to the location and nature of the imbalance. Individuals adhering to this belief might seek treatments such as acupuncture, herbal remedies, or energy healing techniques to restore balance and alleviate the tinnitus.
These varied cultural interpretations highlight the complex interplay between physical sensations and belief systems. While medical explanations for ringing in the ears exist, cultural beliefs provide alternative frameworks for understanding and responding to the symptom. These frameworks can influence help-seeking behavior, coping strategies, and overall perception of the experience, underscoring the importance of cultural sensitivity in addressing concerns related to “si te zumba el oido derecho que significa.”
Frequently Asked Questions Regarding Ringing in the Right Ear
The following questions address common concerns associated with the sensation of tinnitus primarily affecting the right ear.
Question 1: Is right ear ringing always indicative of a serious medical condition?
While persistent or severe tinnitus warrants medical evaluation, not all instances of right ear ringing signify a serious underlying condition. Transient tinnitus can result from temporary factors such as noise exposure or stress. A comprehensive audiological assessment is necessary to determine the cause and severity.
Question 2: Can medication induce right ear ringing?
Certain medications possess ototoxic properties, potentially causing or exacerbating tinnitus. Aspirin, some antibiotics, and chemotherapy drugs are examples of medications linked to tinnitus. Consultation with a physician is advised to review current medications and assess their potential impact on auditory health.
Question 3: How does stress influence the perception of right ear ringing?
Stress and anxiety can amplify the perception of tinnitus. The physiological effects of stress, such as increased muscle tension and altered neural activity, can heighten sensitivity to internal sounds. Stress management techniques may provide relief from tinnitus symptoms.
Question 4: What are the primary treatment options for chronic tinnitus localized to the right ear?
Treatment options vary depending on the underlying cause and severity of the tinnitus. Strategies may include hearing aids, sound therapy, cognitive behavioral therapy, and medication. A personalized treatment plan should be developed in consultation with an audiologist or physician.
Question 5: Is there a definitive cure for right ear ringing?
A universal cure for tinnitus does not currently exist. Management strategies focus on reducing the perceived loudness and intrusiveness of the sound, improving coping mechanisms, and addressing any underlying medical or psychological factors contributing to the symptom. Research into new treatments is ongoing.
Question 6: When should medical attention be sought for right ear ringing?
Medical evaluation is recommended if the tinnitus is sudden in onset, persistent, accompanied by hearing loss or dizziness, or associated with other neurological symptoms. Prompt assessment can help identify and address any underlying medical conditions contributing to the tinnitus.
Understanding the potential causes, management options, and psychological impact of right ear ringing is crucial for effective coping and improved quality of life.
The subsequent section delves into strategies for proactively managing and mitigating the effects of tinnitus.
Concluding Remarks on “Si te zumba el oido derecho que significa”
The exploration of “si te zumba el oido derecho que significa” has revealed a multifaceted phenomenon encompassing medical, neurological, psychological, and cultural dimensions. The perception of right ear ringing warrants thorough investigation to identify potential underlying causes and implement appropriate management strategies. Understanding the subjective experience and addressing associated psychological distress are paramount for improving overall well-being.
Given the complex interplay of factors contributing to tinnitus, a collaborative approach involving medical professionals, audiologists, and mental health specialists is essential. Continued research into the mechanisms underlying tinnitus and the development of effective treatments remain critical for alleviating the burden of this condition and enhancing the quality of life for affected individuals.