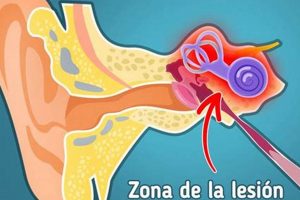
The sensation of ringing in the ears, often described as buzzing, hissing, or clicking sounds, is a common auditory phenomenon. This experience can manifest as a temporary occurrence or persist as a chronic condition. It’s crucial to understand the potential causes and appropriate responses when experiencing this condition, which medical professionals refer to as tinnitus. For instance, loud noise exposure at a concert might induce temporary ringing, while persistent tinnitus could signal underlying medical issues requiring investigation.
Addressing ear ringing effectively is important for several reasons. It can significantly impact quality of life, disrupting sleep, concentration, and emotional well-being. Identifying the triggers and managing associated symptoms can improve daily functioning and prevent potential complications. Historically, remedies for ear ringing have ranged from folk cures to advanced audiological interventions, reflecting the evolving understanding of this complex condition and its impact on individuals.
The subsequent sections will delve into practical steps one can take to alleviate ear ringing, explore potential medical interventions, and provide guidance on when seeking professional medical advice is necessary. Furthermore, this article will explore preventative measures to minimize the risk of experiencing this aural discomfort.
Addressing Ringing in the Ears
Ringing in the ears can be a disruptive and concerning experience. Implementing specific strategies can help manage and potentially alleviate the discomfort associated with this auditory phenomenon.
Tip 1: Sound Therapy: Employ external sounds to mask the perceived ringing. Options include white noise machines, ambient music, or even a fan. The goal is to divert attention from the internal noise, reducing its perceived intensity.
Tip 2: Limit Exposure to Loud Noises: Excessive noise is a significant contributor to ear ringing. Using earplugs or earmuffs in noisy environments, such as concerts or workplaces with heavy machinery, protects auditory health.
Tip 3: Manage Stress and Anxiety: Psychological stress can exacerbate ringing in the ears. Techniques such as deep breathing exercises, meditation, or yoga can help manage stress levels, potentially reducing symptom severity.
Tip 4: Review Medications: Certain medications can have ototoxic effects, meaning they can damage the inner ear and contribute to ringing. Consult with a healthcare provider to review current medications and explore potential alternatives if indicated.
Tip 5: Limit Caffeine and Alcohol Intake: These substances can affect blood flow and neural activity, potentially worsening ear ringing. Reducing or eliminating caffeine and alcohol consumption may provide relief.
Tip 6: Address Underlying Medical Conditions: Ringing in the ears can sometimes be a symptom of an underlying medical condition, such as high blood pressure, temporomandibular joint (TMJ) disorder, or thyroid problems. Seek medical evaluation to rule out and manage any contributing health issues.
Tip 7: Practice Relaxation Techniques: Muscle tension, particularly in the neck and jaw, can contribute to ear ringing. Regularly practicing relaxation techniques like progressive muscle relaxation can help alleviate this tension.
By implementing these strategies, individuals experiencing ringing in the ears may find relief and improve their overall well-being. It’s essential to remember that these are general recommendations, and individualized approaches may be necessary based on the specific cause and severity of the condition.
The following section will discuss when it is essential to consult with a healthcare professional regarding persistent or worsening ear ringing.
1. Identify potential triggers
The process of identifying potential triggers is a cornerstone of managing the experience of ear ringing, often referred to medically as tinnitus. Recognizing the specific factors that exacerbate or initiate the sensation of ringing is crucial for developing effective coping strategies. A failure to identify these triggers may lead to a continuation or intensification of the auditory disturbance, negatively impacting an individuals quality of life. Cause-and-effect relationships are central to this identification process. For example, an individual may notice a marked increase in tinnitus following exposure to loud music, suggesting that noise exposure is a significant trigger. Similarly, certain medications or dietary habits could contribute to heightened sensitivity to the ringing.
The importance of identifying triggers lies in the ability to implement proactive measures. For example, if stress is identified as a major contributor, the individual can actively engage in stress-reduction techniques, such as meditation or exercise. If specific foods or beverages are implicated, dietary modifications can be made. Furthermore, understanding the triggers enables informed discussions with healthcare professionals, potentially leading to targeted medical interventions or adjustments in medication regimens. Failing to pinpoint these triggers often results in a trial-and-error approach to symptom management, which can be frustrating and ineffective. Real-life examples underscore the practical significance of this understanding. A musician, consistently exposed to high sound levels, may adopt protective hearing measures once the connection between noise and tinnitus is established. Alternatively, a patient noticing a correlation between caffeine consumption and ear ringing may opt to reduce or eliminate caffeine intake.
In summary, identifying potential triggers is a foundational step in addressing and mitigating the sensation of ear ringing. This process empowers individuals to take control of their condition by implementing targeted lifestyle modifications and engaging in informed discussions with healthcare providers. While identifying triggers may not always eliminate tinnitus entirely, it can significantly reduce its impact on daily life and overall well-being. The challenge lies in diligently monitoring individual experiences, maintaining detailed records, and remaining open to exploring various potential contributing factors. This proactive approach aligns with a broader strategy of self-management and patient empowerment in the context of chronic auditory conditions.
2. Seek audiological evaluation
An audiological evaluation is a crucial step when experiencing ringing in the ears, a condition known as tinnitus. It serves as a gateway to understanding the underlying causes and developing an appropriate management plan. Ignoring persistent tinnitus without seeking professional assessment can lead to delayed diagnosis of treatable conditions and potentially worsen the impact on quality of life.
- Identifying Underlying Hearing Loss
An audiological evaluation includes comprehensive hearing tests to detect any degree of hearing loss, which is a common co-occurrence with tinnitus. The presence and nature of hearing loss influence the type of tinnitus management strategies that are most likely to be effective. For instance, individuals with high-frequency hearing loss may benefit from hearing aids that amplify those frequencies, effectively reducing the perceived intensity of the tinnitus.
- Ruling Out Medical Causes
Tinnitus can sometimes be a symptom of underlying medical conditions, such as Meniere’s disease, acoustic neuroma, or vascular disorders. An audiologist can conduct tests to help rule out these medical causes or refer the individual to a physician for further evaluation. Early detection of such conditions is crucial for timely medical intervention and preventing potential complications.
- Determining Tinnitus Characteristics
Audiological testing helps characterize the specific features of the tinnitus, such as its pitch, loudness, and location. This information is valuable in selecting appropriate sound therapy techniques and counseling strategies. Understanding the specific characteristics of the tinnitus allows for a more personalized and targeted approach to management.
- Developing a Management Plan
Based on the findings of the audiological evaluation, an audiologist can develop a comprehensive management plan that may include sound therapy, counseling, hearing aids, or referral to other specialists. The plan is tailored to the individual’s specific needs and circumstances, with the goal of reducing the impact of tinnitus on their daily life. For example, an individual may benefit from tinnitus retraining therapy (TRT), which aims to habituate the individual to the tinnitus sound.
In summary, seeking an audiological evaluation is an essential step for individuals experiencing tinnitus. It provides valuable information about the underlying causes, characteristics, and potential management strategies. By undergoing a thorough assessment, individuals can gain a better understanding of their condition and work with an audiologist to develop a personalized plan that improves their quality of life. This proactive approach is far more effective than ignoring the symptom or relying on unproven remedies.
3. Explore sound therapy options
Sound therapy presents a viable strategy for individuals experiencing the sensation of ringing in the ears. This approach aims to mitigate the perceived distress associated with the sound by introducing external auditory stimuli, thereby altering the individual’s perception and response to the tinnitus.
- White Noise Generation
The use of white noise involves the introduction of a consistent, broad-spectrum sound intended to mask or camouflage the tinnitus. This background noise can reduce the contrast between the tinnitus and the surrounding auditory environment, making the ringing less noticeable. Examples include running a fan, using a white noise machine, or tuning into static on a radio. The effectiveness of white noise varies depending on the individual’s specific tinnitus characteristics and personal preferences. It is readily accessible and non-invasive.
- Nature Sounds and Ambient Music
Nature sounds, such as rainfall, ocean waves, or forest ambiance, can provide a more pleasant and calming alternative to white noise. Ambient music, characterized by its soft and unobtrusive nature, can also serve as an effective masking tool. These sounds offer a distracting stimulus that is often perceived as more soothing and less monotonous than white noise. Individuals experiencing heightened anxiety alongside tinnitus may find these options particularly beneficial.
- Tinnitus Masking Devices
Tinnitus masking devices are specialized electronic devices that generate a customized sound designed to specifically target and mask the individual’s tinnitus frequency. These devices are often prescribed by audiologists and tailored to the specific characteristics of the tinnitus, offering a more precise and potentially effective form of sound therapy. They are typically worn in the ear and can be adjusted to provide optimal masking without completely eliminating external sounds.
- Tinnitus Retraining Therapy (TRT)
TRT is a comprehensive approach that combines sound therapy with counseling to habituate individuals to their tinnitus. This involves using broadband noise generators at a low level combined with directive counseling to change the individual’s perception and reaction to the tinnitus. The goal is to reduce the distress and annoyance associated with the ringing, rather than completely eliminating the sound. TRT requires a commitment to long-term therapy and is typically administered by audiologists specifically trained in this technique.
The selection of an appropriate sound therapy option requires careful consideration of individual preferences, tinnitus characteristics, and the presence of any co-existing hearing loss. While sound therapy does not cure tinnitus, it can significantly improve the individual’s ability to manage the condition and reduce its impact on daily life. Consulting with an audiologist is recommended to determine the most suitable approach and to ensure proper fitting and adjustment of any sound-generating devices.
4. Manage associated stress
Stress management plays a critical role in mitigating the subjective experience of ear ringing, commonly known as tinnitus. Elevated stress levels can exacerbate the perception of tinnitus, making it more intrusive and bothersome. Therefore, strategies aimed at reducing stress are an integral component of a comprehensive approach to managing this condition.
- Physiological Impact of Stress
Stress triggers the release of cortisol and other stress hormones, which can increase blood pressure and muscle tension, potentially worsening tinnitus symptoms. Chronic stress can lead to prolonged activation of the sympathetic nervous system, further amplifying the perception of auditory disturbances. Implementing relaxation techniques can counteract these physiological effects, reducing the intensity of the perceived ringing.
- Cognitive and Emotional Regulation
Stress often leads to negative thought patterns and heightened emotional reactivity, which can exacerbate the annoyance and distress associated with tinnitus. Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) techniques, such as cognitive restructuring and mindfulness practices, can help individuals challenge negative thoughts and develop more adaptive coping strategies. By managing cognitive and emotional responses to tinnitus, individuals can reduce its perceived impact on their overall well-being.
- Lifestyle Modifications for Stress Reduction
Adopting healthy lifestyle habits, such as regular exercise, sufficient sleep, and a balanced diet, can significantly reduce overall stress levels and improve the body’s resilience to stressors. Avoiding stimulants like caffeine and nicotine, which can exacerbate both stress and tinnitus, is also crucial. Incorporating these lifestyle modifications into a daily routine can promote a sense of control and well-being, indirectly mitigating the effects of tinnitus.
- Mindfulness and Relaxation Techniques
Practicing mindfulness meditation, deep breathing exercises, or progressive muscle relaxation can help individuals cultivate a sense of calm and reduce physiological arousal. These techniques promote present-moment awareness and decrease the tendency to ruminate on negative thoughts about tinnitus. Regular engagement in mindfulness practices can lead to a gradual reduction in stress-related tinnitus symptoms over time.
The management of associated stress is not a standalone solution but rather an integral component of a holistic approach to addressing ear ringing. While stress reduction techniques may not eliminate the tinnitus entirely, they can significantly improve an individual’s ability to cope with the condition and reduce its impact on daily life. By combining stress management with other strategies, such as sound therapy and audiological evaluation, individuals can achieve a more comprehensive and effective management of their tinnitus symptoms.
5. Consider medical intervention
When experiencing persistent or debilitating ear ringing, often described as “que hacer cuando te zumba el oido,” considering medical intervention becomes a critical step. This is particularly relevant when self-management strategies prove insufficient in alleviating the discomfort or when the underlying cause remains unidentified. Medical intervention encompasses a range of diagnostic and therapeutic approaches aimed at addressing the root cause and mitigating the symptoms of tinnitus.
- Pharmacological Management
Certain medications may be prescribed to manage the symptoms of tinnitus, particularly when associated with anxiety, depression, or sleep disturbances. These medications might include tricyclic antidepressants, anti-anxiety drugs, or sleep aids. While these medications do not directly eliminate tinnitus, they can improve an individual’s ability to cope with the condition and reduce its impact on daily life. It’s important to note that pharmacological management is typically considered when other conservative measures have been exhausted, and it requires careful monitoring by a healthcare professional due to potential side effects.
- Surgical Options
In rare cases, tinnitus may be caused by an underlying medical condition that requires surgical intervention. Examples include acoustic neuroma, a benign tumor on the auditory nerve, or temporomandibular joint (TMJ) disorders. Surgical removal of the tumor or correction of TMJ dysfunction may alleviate the tinnitus symptoms. However, surgery is typically reserved for cases where a specific anatomical cause of the tinnitus can be identified and addressed surgically.
- Cochlear Implants
For individuals with severe hearing loss and tinnitus, a cochlear implant may be considered. Cochlear implants bypass the damaged parts of the inner ear and directly stimulate the auditory nerve, providing a sense of hearing and often reducing the perception of tinnitus. This option is typically reserved for individuals who meet specific audiological criteria and have not benefited from other tinnitus management strategies.
- Tinnitus Retraining Therapy (TRT) with Audiological Support
When tinnitus is significantly impacting quality of life, Tinnitus Retraining Therapy, facilitated by qualified audiologists or healthcare professionals, is considered a medical intervention.TRT aims to habituate individuals to their tinnitus, reducing their reaction to the sound. This process involves a combination of directive counseling and sound therapy, with the intention of retraining the brain to filter out the tinnitus signal. TRT typically requires a long-term commitment and active participation from the individual. Audiological support and monitoring are essential throughout the therapy process.
Consideration of medical intervention in the context of “que hacer cuando te zumba el oido” underscores the importance of seeking professional medical advice when self-management strategies are insufficient. The appropriate medical intervention will vary depending on the underlying cause, severity of symptoms, and individual patient characteristics. A thorough medical evaluation is essential to determine the most appropriate course of action and ensure that potential benefits outweigh the risks associated with any medical intervention.
Frequently Asked Questions
The following questions address common concerns related to the sensation of ringing in the ears. The information presented is intended for educational purposes and should not substitute professional medical advice.
Question 1: Is the sensation of ear ringing always indicative of a serious underlying medical condition?
Not necessarily. While ear ringing can sometimes be a symptom of an underlying medical problem, it is frequently associated with factors such as noise exposure, stress, or medication side effects. A thorough medical evaluation is recommended to determine the specific cause.
Question 2: What immediate steps can be taken to alleviate the sensation of ear ringing?
Initial measures may include finding a quiet environment, employing sound masking techniques using white noise or ambient sounds, and avoiding potential triggers such as caffeine or loud noises. If the ringing persists, seeking professional audiological or medical advice is advised.
Question 3: Are there specific dietary recommendations to reduce the occurrence of ear ringing?
While no specific dietary regimen guarantees a reduction in ear ringing, maintaining a balanced diet, limiting sodium intake, and avoiding excessive consumption of caffeine and alcohol may be beneficial. Certain food sensitivities may also contribute to the condition; therefore, monitoring dietary responses can be useful.
Question 4: Can stress and anxiety significantly impact the experience of ear ringing?
Yes, stress and anxiety can exacerbate the perception of ear ringing. Implementing stress-reduction techniques, such as mindfulness meditation or relaxation exercises, may help manage the intensity and frequency of the sensation.
Question 5: What types of healthcare professionals specialize in the diagnosis and management of ear ringing?
Audiologists are the primary healthcare professionals specializing in the evaluation and management of ear ringing. They can perform comprehensive hearing tests and recommend appropriate interventions, such as sound therapy or hearing aids. In some cases, referral to an otolaryngologist (ENT specialist) or neurologist may be necessary.
Question 6: Is there a definitive cure for the sensation of ear ringing?
A definitive cure for ear ringing is not always possible, particularly if the underlying cause is not readily identifiable or treatable. However, various management strategies, including sound therapy, counseling, and medical interventions, can significantly improve an individual’s ability to cope with the condition and reduce its impact on daily life.
Understanding the complexities of ear ringing, including potential causes and available management options, is essential for effective coping and improved quality of life. A proactive and informed approach is recommended.
The subsequent section provides insights on preventative measures to reduce the risk of experiencing ear ringing.
Addressing Persistent Ringing in the Ears
The exploration of que hacer cuando te zumba el oido reveals a multifaceted approach to managing this auditory phenomenon. From identifying potential triggers and seeking professional audiological evaluation to exploring sound therapy options and considering medical interventions, effective management hinges on a comprehensive understanding of the individual’s specific circumstances and the potential underlying causes. The content detailed outlines various methods for mitigating the distress caused by ringing, buzzing or other sensations in the ears, with an emphasis on both immediate relief and long-term management strategies.
The persistent sensation of que hacer cuando te zumba el oido can severely impact an individuals overall well-being. Therefore, individuals experiencing chronic or worsening symptoms should seek professional medical advice to prevent further complications, explore potential treatments, and improve their quality of life. Recognizing the seriousness of the condition and adopting a proactive approach are crucial steps toward mitigating its impact and maintaining optimal auditory health.