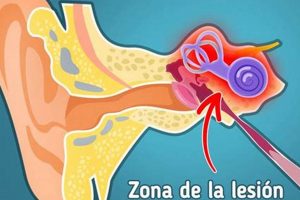
Tinnitus, characterized by the perception of sound when no external noise is present, can manifest as ringing, buzzing, hissing, or clicking. During gestation, experiencing these auditory sensations is not uncommon. The origins of this phenomenon during this specific physiological state are multifaceted and warrant careful examination.
The occurrence during this period is often linked to hormonal fluctuations, increased blood volume, and changes in blood pressure. These physiological alterations can affect the inner ear’s delicate structures and neural pathways, leading to the subjective experience of sounds. Identifying potential contributing factors like stress, anxiety, dietary habits, and pre-existing conditions such as hypertension is crucial for comprehensive management.
This article will explore the various reasons behind auditory disturbances during pregnancy, examining both physiological changes and potential underlying conditions. It will also address diagnostic approaches and management strategies aimed at alleviating discomfort and ensuring maternal well-being.
Addressing Auditory Disturbances During Pregnancy
Managing subjective auditory sensations during gestation requires a multi-faceted approach focused on identifying potential causes and mitigating discomfort. These recommendations are designed to offer strategies for expectant mothers experiencing such symptoms.
Tip 1: Monitor Blood Pressure Regularly: Consistent monitoring of blood pressure is crucial, as hypertension can exacerbate or trigger auditory disturbances. Consult with a healthcare provider for appropriate management if elevated blood pressure is detected.
Tip 2: Evaluate Iron Levels: Iron deficiency anemia can contribute to tinnitus. A blood test can determine iron levels, and supplementation, under medical supervision, may be beneficial if a deficiency is found.
Tip 3: Manage Stress and Anxiety: Implement relaxation techniques such as deep breathing exercises, meditation, or prenatal yoga to reduce stress and anxiety levels. Chronic stress can worsen subjective auditory sensations.
Tip 4: Maintain Adequate Hydration: Ensure sufficient fluid intake throughout the day. Dehydration can affect blood volume and circulation, potentially impacting inner ear function.
Tip 5: Review Medication List: Consult with a healthcare provider to review all current medications, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements. Certain substances can be ototoxic and may contribute to the issue.
Tip 6: Limit Caffeine and Sodium Intake: Reducing caffeine and sodium consumption may help regulate blood pressure and fluid balance, potentially alleviating auditory discomfort.
Tip 7: Seek Professional Audiological Evaluation: If symptoms persist or worsen, consult an audiologist for a comprehensive hearing evaluation to rule out any underlying auditory pathology.
Adhering to these guidelines can potentially mitigate the impact of these symptoms, contributing to improved well-being throughout pregnancy. It is crucial to consult a healthcare professional for personalized advice and to address any underlying medical conditions.
The subsequent sections will delve into diagnostic procedures and treatment options available for managing this condition effectively.
1. Hormonal fluctuations
Hormonal fluctuations during pregnancy represent a significant factor contributing to auditory sensations, characterized by the perception of sound in the absence of an external source. The elevated levels of estrogen and progesterone, essential for maintaining pregnancy, exert effects on various physiological systems, including blood volume and fluid balance. These hormonal shifts can influence the intricate structures of the inner ear and the auditory pathways, leading to subjective auditory experiences. For instance, the heightened fluid retention associated with increased estrogen can potentially elevate pressure within the inner ear, triggering or exacerbating tinnitus-like symptoms.
These hormonal changes are not uniform across all pregnancies, and individual sensitivity to these shifts varies. Some expectant mothers may experience a noticeable increase in auditory disturbances, while others may remain unaffected. It is also important to consider the potential for underlying conditions, such as thyroid imbalances, which can further amplify the impact of hormonal fluctuations on the auditory system. Consequently, a thorough evaluation that considers both hormonal profiles and pre-existing conditions is crucial for understanding and managing auditory discomfort during pregnancy.
In summary, hormonal fluctuations significantly affect the auditory system during pregnancy. While these changes are generally physiological, their impact can vary considerably. Understanding this connection is vital for healthcare providers to accurately assess and manage auditory symptoms, ensuring both maternal comfort and well-being throughout the gestational period.
2. Increased blood volume
The physiological changes associated with pregnancy include a significant increase in blood volume, typically ranging from 30% to 50% above pre-pregnancy levels. This expansion in circulatory fluid is essential to meet the metabolic demands of both the mother and the developing fetus. However, this augmented blood volume can exert pressure on various bodily systems, including the auditory system. The delicate structures within the inner ear, responsible for auditory transduction and balance, are particularly susceptible to changes in vascular pressure. Consequently, the subjective perception of sound, often described as ringing, buzzing, or hissing, may arise due to increased pressure affecting cochlear function and the associated neural pathways.
The increased blood volume can lead to altered blood flow dynamics within the inner ear’s microvasculature. This altered flow can disrupt the delicate balance of fluids and electrolytes essential for proper auditory nerve function. Moreover, elevated blood pressure, which can accompany increased blood volume, may further exacerbate the issue. For example, an expectant mother with pre-existing hypertension could experience a more pronounced occurrence of auditory sensations due to the compounded effects of increased blood volume and already elevated blood pressure. Recognizing this connection is vital for healthcare providers when assessing auditory complaints during pregnancy. Diagnostic efforts should include blood pressure monitoring and evaluation for potential underlying cardiovascular contributions.
In summary, increased blood volume during pregnancy can contribute to auditory sensations through its impact on inner ear pressure and blood flow. While typically a benign physiological adaptation, its effects can be significant and warrant careful evaluation, particularly in individuals with pre-existing conditions. Understanding this link allows for targeted management strategies, focusing on blood pressure control and overall cardiovascular health, to alleviate discomfort and ensure maternal well-being.
3. Blood pressure changes
Blood pressure fluctuations are a common physiological adaptation during gestation and represent a significant factor in understanding auditory disturbances experienced during this period. The relationship is complex, with both increases and decreases in blood pressure potentially contributing to the onset of tinnitus or other abnormal auditory perceptions. Elevated blood pressure, a condition frequently observed during pregnancy, can increase vascular pressure within the delicate structures of the inner ear, disrupting the normal function of the cochlea and auditory nerve. Conversely, sudden drops in blood pressure can compromise blood flow to the inner ear, also leading to auditory disturbances. The intensity and characteristics of the perceived sound can vary depending on the magnitude and duration of these blood pressure variations. For instance, a pregnant individual with gestational hypertension may report a pulsating tinnitus, synchronized with their heartbeat, reflecting the increased pressure within the auditory vasculature.
Further exacerbating the issue is the potential interplay between blood pressure medications and auditory function. Certain antihypertensive drugs, while necessary for managing maternal hypertension, can have ototoxic effects, potentially contributing to or worsening existing auditory symptoms. This necessitates careful consideration of medication choices and dosage adjustments under the guidance of a qualified healthcare professional. Moreover, conditions like pre-eclampsia, characterized by dangerously high blood pressure and potential organ damage, can significantly increase the risk of auditory complications. Early detection and management of blood pressure abnormalities are, therefore, critical not only for maternal and fetal well-being but also for preserving auditory health. Real-life examples include expectant mothers reporting relief from tinnitus after blood pressure stabilization through medication or lifestyle modifications, highlighting the direct link between blood pressure control and auditory symptom alleviation.
In summary, blood pressure alterations during pregnancy can significantly influence auditory function. Elevated or reduced blood pressure, the use of certain medications, and conditions such as pre-eclampsia can all contribute to auditory disturbances. Recognizing this connection underscores the importance of routine blood pressure monitoring, appropriate medical management, and careful consideration of ototoxic medication risks. A comprehensive approach that addresses blood pressure control is essential for alleviating auditory discomfort and ensuring optimal maternal health throughout pregnancy.
4. Inner ear effects
The inner ear’s intricate structures are highly susceptible to the physiological changes accompanying gestation, thereby establishing a direct link with auditory disturbances experienced during pregnancy. The cochlea, responsible for transducing sound vibrations into neural signals, and the vestibular system, responsible for balance, are both sensitive to alterations in fluid pressure, blood flow, and hormonal levels. These changes can disrupt the normal function of these structures, leading to the perception of phantom sounds, commonly described as ringing, buzzing, or hissing. For example, increased fluid retention during pregnancy can elevate pressure within the inner ear, stimulating the hair cells responsible for auditory transduction, even in the absence of external sound stimuli. This highlights the direct cause-and-effect relationship between inner ear physiological changes and the perception of abnormal auditory sensations.
Understanding the importance of inner ear effects in the context of auditory disturbances during pregnancy has practical significance for diagnosis and management. Accurate diagnosis requires thorough audiological evaluation to rule out pre-existing conditions or structural abnormalities. Management strategies may focus on mitigating contributing factors, such as controlling blood pressure, managing fluid balance, and addressing underlying inflammation. For instance, if inner ear inflammation is suspected, a healthcare provider may recommend anti-inflammatory interventions, while carefully monitoring for potential adverse effects on the pregnancy. Such targeted approaches underscore the practical benefit of recognizing inner ear physiology as a critical component of auditory disturbances during gestation.
In summary, alterations within the inner ear are a significant contributor to auditory sensations reported during pregnancy. The delicate structures are vulnerable to fluctuations in fluid pressure, blood flow, and hormonal levels, which can disrupt normal auditory and vestibular function. Recognizing this connection is critical for accurate diagnosis and targeted management strategies, aimed at alleviating symptoms and improving maternal well-being. However, the challenge lies in differentiating between physiological changes and underlying pathology, necessitating careful evaluation and monitoring throughout the gestational period.
5. Stress, anxiety
Experiencing heightened stress and anxiety during gestation can significantly contribute to the perception of auditory disturbances. These psychological states trigger physiological responses, including the release of cortisol and adrenaline, which affect blood pressure, heart rate, and muscle tension. These responses can disrupt the normal functioning of the auditory system, leading to the subjective sensation of sound, often described as tinnitus. The amplification of pre-existing conditions due to stress, coupled with hormonal shifts, exemplifies this connection. For instance, an expectant mother with a history of anxiety may find that her tinnitus symptoms intensify during periods of increased stress, impacting sleep and overall well-being. This highlights the role of psychological factors in mediating auditory experiences.
The practical significance of understanding this relationship lies in the implementation of stress-reduction techniques as a management strategy. Mindfulness practices, prenatal yoga, and cognitive behavioral therapy can mitigate the physiological impact of stress and anxiety, potentially alleviating auditory symptoms. Furthermore, identifying and addressing the underlying sources of stress through counseling or support groups can offer long-term relief. The efficacy of these interventions demonstrates the direct influence of psychological well-being on auditory perception. An expectant mother who integrates relaxation exercises into her daily routine may experience a reduction in the frequency and intensity of tinnitus episodes, improving quality of life throughout pregnancy.
In summary, the connection between stress, anxiety, and auditory disturbances during pregnancy underscores the complex interplay between psychological and physiological processes. Stress and anxiety exacerbate existing conditions or trigger new symptoms. Management approaches focus on reducing stress and anxiety, mitigating their negative effects on auditory experiences. This understanding emphasizes the need for a holistic approach to prenatal care, addressing both physical and mental well-being for optimal maternal health.
6. Dietary influences
The dietary choices made during gestation can influence the likelihood and intensity of auditory sensations, specifically tinnitus, experienced by pregnant individuals. Deficiencies in essential nutrients and excessive consumption of certain substances can disrupt inner ear function, contributing to the onset or exacerbation of tinnitus. Dietary influences encompass both direct effects on auditory structures and indirect effects through systemic changes. Insufficient iron intake, leading to anemia, can compromise oxygen delivery to the inner ear, impairing cellular function and potentially triggering tinnitus. Similarly, inadequate intake of B vitamins, particularly B12, may affect nerve function, including the auditory nerve, thus contributing to auditory disturbances. Conversely, excessive consumption of sodium can elevate blood pressure, increasing pressure within the inner ear’s delicate vessels, and potentially inducing tinnitus. Furthermore, stimulants such as caffeine can exacerbate auditory sensitivity and contribute to the perception of phantom sounds.
Real-life examples illustrate the connection between dietary choices and tinnitus during pregnancy. An expectant mother with pre-existing iron deficiency anemia, who continues to have inadequate iron intake, may experience a worsening of tinnitus symptoms. Addressing the iron deficiency through dietary modifications or supplementation, under medical supervision, can often lead to symptom alleviation. Similarly, pregnant individuals who consume excessive amounts of processed foods high in sodium may find that limiting sodium intake reduces the intensity and frequency of tinnitus episodes. The practical significance of this understanding lies in the potential for dietary modifications to serve as a non-pharmacological approach to managing auditory disturbances during pregnancy. Dietary counseling, tailored to address individual needs and nutritional deficiencies, can empower expectant mothers to proactively manage their symptoms through informed dietary choices.
In summary, dietary influences can significantly affect the occurrence and intensity of auditory sensations during gestation. Deficiencies in essential nutrients, excessive sodium intake, and stimulant consumption can all contribute to tinnitus. By addressing dietary imbalances and promoting informed nutritional choices, healthcare providers can help manage symptoms and improve the overall well-being of pregnant individuals. It’s important to note that dietary modifications should always be implemented under the guidance of a healthcare professional to ensure the safety and nutritional adequacy of the pregnancy diet.
Frequently Asked Questions Regarding Auditory Sensations During Pregnancy
This section addresses common inquiries surrounding auditory disturbances, particularly those resembling tinnitus, that may occur during pregnancy. The aim is to provide clear, factual information to enhance understanding and guide appropriate action.
Question 1: What is the underlying cause of auditory sensations, often described as “ringing” or “buzzing”, during pregnancy?
The perception of auditory sensations, absent of external stimuli, during gestation is often multifactorial. Hormonal fluctuations, increased blood volume, and changes in blood pressure are potential contributing factors. In some instances, underlying conditions may also play a role.
Question 2: Are these auditory sensations a common occurrence during pregnancy?
Experiencing auditory disturbances is not uncommon during pregnancy. Physiological changes associated with gestation can impact the auditory system, leading to subjective sound perceptions.
Question 3: When should a healthcare professional be consulted regarding these auditory sensations?
Consultation with a healthcare provider is advisable if auditory sensations are persistent, bothersome, or accompanied by other symptoms, such as dizziness, hearing loss, or headache.
Question 4: Can dietary modifications help alleviate auditory sensations during pregnancy?
In some cases, dietary adjustments may be beneficial. Maintaining adequate iron intake, limiting sodium consumption, and avoiding excessive caffeine may help mitigate symptoms. However, dietary changes should be implemented under medical supervision.
Question 5: Are there specific medications to avoid during pregnancy due to their potential impact on auditory function?
Certain medications are known to have ototoxic effects and should be avoided during pregnancy unless specifically prescribed by a healthcare provider. A thorough review of all medications, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements, is essential.
Question 6: Can stress and anxiety contribute to auditory disturbances during pregnancy?
Elevated stress and anxiety levels can exacerbate auditory symptoms. Implementing stress-reduction techniques, such as mindfulness practices and relaxation exercises, may offer some relief.
In summary, auditory disturbances experienced during gestation can stem from various physiological changes and other factors. Medical evaluation is necessary to determine appropriate management strategies and ensure maternal well-being.
The subsequent sections will delve into diagnostic procedures and treatment options available for managing this condition effectively.
Conclusion
The investigation into porque zumba el odo en el embarazo reveals a complex interplay of physiological factors contributing to this auditory phenomenon. Hormonal shifts, augmented blood volume, blood pressure fluctuations, inner ear effects, alongside the impact of stress, anxiety, and dietary choices, all converge to influence auditory perception during gestation. Comprehensive understanding of these interconnected elements is crucial for both expectant mothers and healthcare providers.
While often benign, persistent or severe auditory disturbances warrant thorough medical evaluation. Identifying underlying causes and implementing targeted management strategies can significantly improve the well-being of pregnant individuals. Continued research and awareness are essential to refine diagnostic approaches and develop effective interventions for this often overlooked aspect of prenatal health. This exploration underscores the importance of holistic prenatal care that addresses both physical and psychological factors contributing to maternal health and auditory wellness.