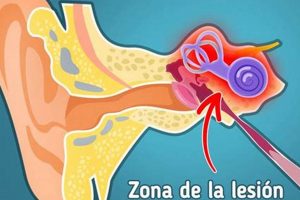
The sensation of ringing, buzzing, or hissing in the ear, specifically the left ear, in the absence of an external sound source is a common auditory phenomenon. This perception, often described as a “zumbido,” can vary in intensity and pitch, and may be intermittent or continuous. It is important to note that various factors can trigger this auditory experience.
Understanding the underlying causes of this auditory perception is beneficial for managing its impact on an individual’s quality of life. While often benign and temporary, persistent or severe instances can be associated with medical conditions or environmental factors. A thorough evaluation of the individual’s medical history, lifestyle, and possible exposure to noise is important for determining potential triggers and appropriate management strategies. Historically, cultures have attributed spiritual or symbolic meanings to such auditory sensations; however, modern medicine focuses on identifying physiological or neurological explanations.
The subsequent sections of this article will delve into the potential medical causes, diagnostic approaches, and management options for this specific auditory phenomenon. These sections will also explore lifestyle modifications and preventative measures that may help reduce the frequency or intensity of this experience.
Addressing the Auditory Sensation
The following guidance addresses the common experience of auditory perception in the left ear characterized as ringing, buzzing, or hissing in the absence of external stimuli. These recommendations are intended to inform and assist in managing the sensation effectively.
Tip 1: Monitor and Record: Maintain a log of when the auditory sensation occurs, noting the time of day, duration, and any associated symptoms such as dizziness, headache, or changes in hearing. This data aids in identifying patterns and potential triggers.
Tip 2: Evaluate Medication Use: Certain medications are known to have ototoxic effects, potentially leading to or exacerbating auditory sensations. Review current medications with a healthcare professional to assess possible contribution.
Tip 3: Manage Stress Levels: Stress can exacerbate the perception of auditory sensations. Employ stress-reduction techniques such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, or regular physical activity to potentially mitigate the sensation’s intensity.
Tip 4: Limit Exposure to Loud Noise: Prolonged or intense exposure to loud noise can damage hearing and worsen auditory sensations. Utilize hearing protection in noisy environments, such as earplugs or earmuffs.
Tip 5: Modify Dietary Habits: Certain substances, including caffeine, alcohol, and excessive salt, may contribute to the sensation. Consider reducing intake of these substances to observe if a reduction in the auditory sensation occurs.
Tip 6: Seek Professional Evaluation: If the auditory sensation is persistent, severe, or accompanied by other concerning symptoms, consult an audiologist or physician for a comprehensive evaluation. Diagnostic testing can help identify underlying medical conditions.
Tip 7: Ensure Adequate Sleep: Sleep deprivation can increase stress and sensitivity to internal sensations. Prioritize consistent sleep schedules and a restful sleep environment to promote overall well-being and potentially reduce the perception of auditory sensations.
Following these tips can empower individuals to better understand and manage the auditory sensation they experience. Implementing lifestyle modifications and seeking professional advice when necessary are important steps in mitigating its impact.
The concluding section of this article will consolidate key information and reiterate the importance of proactive management and consultation with healthcare professionals regarding this auditory experience.
1. Subjective auditory hallucination
The experience of “que es cuando te zumba el oido izquierdo” aligns with the definition of a subjective auditory hallucination, in that it involves perceiving soundspecifically a buzzing or ringingin the absence of an external acoustic stimulus. The term “subjective” is critical, highlighting that the auditory event originates within the individual’s auditory system or brain, and is not an objective, verifiable sound source. The perception is a creation of the nervous system rather than a response to an external trigger.
The importance of recognizing “que es cuando te zumba el oido izquierdo” as a form of subjective auditory hallucination lies in the diagnostic and therapeutic implications. It shifts the focus from searching for external sources of sound to investigating the internal mechanisms that may be causing the perception. For instance, damage to the inner ear, auditory nerve dysfunction, or even altered brain activity in auditory processing centers can manifest as a “zumbido” or ringing. Moreover, conditions such as temporomandibular joint (TMJ) disorders or muscular tension in the neck can indirectly affect the auditory system, leading to this subjective auditory experience. Understanding the phenomenon through this lens allows healthcare professionals to consider a wider range of potential etiologies and appropriate interventions, including audiological assessments, neurological examinations, and psychological evaluations to address contributing factors such as stress or anxiety.
In conclusion, recognizing “que es cuando te zumba el oido izquierdo” as a subjective auditory hallucination is essential for accurate diagnosis and effective management. It emphasizes the internal origin of the sound perception, prompting a comprehensive evaluation of the individual’s auditory and neurological systems. This approach leads to targeted interventions, ultimately improving the individual’s quality of life by reducing the impact of the auditory disturbance. Future research could explore the specific neural pathways involved in generating these subjective sounds, potentially leading to more refined and effective treatment strategies.
2. Possible underlying cause
The occurrence of “que es cuando te zumba el oido izquierdo” commonly indicates the presence of an underlying factor influencing auditory perception. This sensation, characterized by ringing or buzzing in the left ear, is rarely spontaneous and often arises as a consequence of another condition or external influence. Establishing the precise etiology is important for devising appropriate management strategies and addressing the root cause of the auditory disturbance. Examples of potential underlying causes include noise-induced hearing damage, Meniere’s disease, temporomandibular joint (TMJ) disorders, medication side effects (ototoxicity), and even neurological conditions such as acoustic neuroma. Determining the specific trigger requires a thorough medical evaluation.
The diagnostic process to identify the “possible underlying cause” of “que es cuando te zumba el oido izquierdo” involves a combination of audiologic testing, medical history review, and potentially imaging studies such as MRI. Audiologic testing assesses the integrity of the auditory system, including hearing thresholds and the function of the inner ear. The medical history provides valuable insights into potential risk factors or pre-existing conditions. Imaging studies are employed to rule out structural abnormalities or neurological causes. Practical application of this understanding allows for targeted treatments, such as hearing aids for noise-induced hearing loss, medication for Meniere’s disease, or physical therapy for TMJ disorders. Addressing the underlying cause aims to alleviate or eliminate the auditory symptom, thereby improving the individual’s quality of life.
Identifying the “possible underlying cause” of “que es cuando te zumba el oido izquierdo” presents diagnostic challenges due to the complexity of the auditory system and the potential for multiple contributing factors. However, precise diagnosis is essential for effective management. By understanding the intricate connection between the auditory symptom and its potential origins, healthcare professionals can implement tailored treatment plans that address the underlying condition, mitigate the perceived ringing or buzzing, and ultimately enhance the patient’s auditory health and overall well-being. The integration of comprehensive medical evaluation with focused management strategies is vital to achieve successful outcomes in individuals experiencing “que es cuando te zumba el oido izquierdo”.
3. Neurological contribution factor
The perception of auditory sensations, characterized by “que es cuando te zumba el oido izquierdo,” can frequently be attributed to neurological contributions. This acknowledges that the generation and interpretation of these phantom sounds involve complex neural pathways within the auditory system and the brain. Instead of originating from an external stimulus or mechanical dysfunction in the ear itself, the “zumbido” may arise from aberrant neural activity, misfiring neurons, or disruptions in the brain’s auditory processing centers. Examples include damage to the auditory nerve, lesions in the brainstem, or altered cortical activity that creates the subjective experience of ringing or buzzing. Furthermore, conditions like multiple sclerosis or certain types of epilepsy, which directly affect the nervous system, can manifest auditory hallucinations as a symptom.
The importance of recognizing neurological contribution as a component of “que es cuando te zumba el oido izquierdo” is multifaceted. It allows for a shift in diagnostic focus, emphasizing the need for neurological evaluations such as MRI scans or electrophysiological studies to identify underlying neural pathologies. This understanding also influences treatment strategies, as therapies aimed at modulating neural activity, such as medications targeting neurotransmitter imbalances or neuromodulation techniques, may be considered. For example, individuals with tinnitus related to neural hyperactivity in the auditory cortex may benefit from transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) to dampen down the aberrant activity. Moreover, recognizing this neurological involvement highlights the potential role of psychological factors, such as stress or anxiety, in modulating neural activity and exacerbating the perceived auditory sensation.
In summary, acknowledging the “neurological contribution factor” in “que es cuando te zumba el oido izquierdo” is essential for comprehensive assessment and management. It necessitates a holistic approach, integrating audiological evaluations with neurological investigations to determine the root cause of the auditory perception. Furthermore, it underscores the potential for tailored treatment strategies that target the underlying neural mechanisms, as well as the role of psychological interventions in managing the subjective experience. The challenges in this area lie in the complexity of the nervous system and the difficulty in precisely identifying the specific neural pathways involved. Nevertheless, continued research into the neurophysiological basis of tinnitus and other auditory hallucinations holds promise for developing more effective and targeted therapies.
4. Stress and exacerbation
Stress is recognized as a significant exacerbating factor in the experience of “que es cuando te zumba el oido izquierdo”. Elevated stress levels, whether stemming from occupational demands, personal relationships, or underlying anxiety disorders, can intensify the perception of ringing, buzzing, or hissing in the left ear. This phenomenon is not solely psychological; physiological responses to stress, such as increased muscle tension, changes in blood pressure, and the release of stress hormones, can directly impact the auditory system. Muscular tension in the neck and jaw, for instance, can affect the function of the Eustachian tube and alter auditory perception. The increase in blood pressure and heart rate can amplify the awareness of internal sounds, thus heightening the perception of tinnitus. For individuals already predisposed to auditory sensitivities or existing tinnitus, stress acts as a catalyst, magnifying the pre-existing condition.
The practical significance of understanding the stress-exacerbation link in “que es cuando te zumba el oido izquierdo” lies in the development of targeted management strategies. Individuals experiencing this auditory sensation often benefit from stress-reduction techniques such as mindfulness meditation, regular exercise, and cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT). These approaches aim to mitigate the physiological and psychological effects of stress, thereby reducing the intensity and frequency of the perceived “zumbido”. In clinical practice, healthcare professionals often recommend a combination of audiological interventions and stress management techniques to provide comprehensive care. For example, an individual working in a high-pressure environment who experiences heightened tinnitus during periods of intense workload may be advised to incorporate relaxation exercises into their daily routine and modify their work habits to reduce overall stress exposure.
In conclusion, the interaction between stress and “que es cuando te zumba el oido izquierdo” is a well-documented phenomenon with tangible implications for management and treatment. By recognizing the role of stress as an exacerbating factor, healthcare professionals can develop personalized interventions that not only address the auditory symptoms directly but also target the underlying stress response. While effectively managing stress may not eliminate the sensation entirely, it can significantly reduce its impact on an individual’s quality of life. Future research may focus on elucidating the precise neural pathways involved in the stress-tinnitus connection, potentially leading to more targeted and effective therapeutic interventions.
5. Impact on daily life
The presence of “que es cuando te zumba el oido izquierdo,” manifesting as ringing, buzzing, or hissing in the left ear, frequently exerts a substantial influence on an individual’s daily activities and overall well-being. This auditory perception, even if intermittent, can significantly disrupt various aspects of life, affecting concentration, sleep patterns, and emotional state. The following points outline specific facets of this impact.
- Cognitive Function
Persistent auditory sensations impair cognitive function by disrupting focus and concentration. The persistent noise can be distracting, making it difficult to concentrate on tasks requiring sustained attention, such as reading, writing, or performing detailed work. This reduced cognitive efficiency can lead to decreased productivity and increased frustration.
- Sleep Disturbance
Auditory disturbances significantly disrupt sleep patterns. The presence of ringing or buzzing in the ear can make it difficult to fall asleep or stay asleep, leading to insomnia and chronic fatigue. Sleep deprivation further exacerbates stress and anxiety, which in turn can worsen the auditory sensation, creating a self-perpetuating cycle.
- Emotional Well-being
The persistent nature of the auditory sensation contributes to emotional distress, including anxiety, irritability, and depression. The inability to escape the constant noise can lead to feelings of helplessness and hopelessness. This emotional burden can negatively affect relationships, social interactions, and overall quality of life.
- Social and Occupational Activities
The impact extends to social and occupational activities. Individuals may avoid social situations due to the discomfort or embarrassment caused by the auditory sensation. Difficulty concentrating can impair work performance, leading to decreased productivity and potential job-related stress. The cumulative effect of these factors can result in social isolation and reduced participation in activities that were previously enjoyable.
In conclusion, the multifaceted impact of “que es cuando te zumba el oido izquierdo” underscores the importance of seeking timely diagnosis and effective management strategies. Addressing both the underlying causes and the symptomatic effects of this auditory phenomenon is essential for mitigating its negative influence on daily life and promoting overall well-being.
6. Management and mitigation
Effective management and mitigation strategies are paramount in addressing the disruptive effects associated with “que es cuando te zumba el oido izquierdo”. These strategies encompass a multifaceted approach aimed at alleviating symptoms, addressing underlying causes, and improving the individual’s overall quality of life. The following facets outline key elements in the management and mitigation of this auditory experience.
- Audiological Evaluation and Intervention
An initial step involves a comprehensive audiological evaluation to assess hearing thresholds, identify potential auditory pathologies, and determine the characteristics of the perceived auditory sensation. Based on the evaluation, interventions such as hearing aids for associated hearing loss or tinnitus maskers can be implemented to reduce the perceived intensity of the “zumbido” and improve auditory perception.
- Pharmacological Management
In certain cases, pharmacological interventions may be considered to manage underlying conditions or alleviate specific symptoms associated with “que es cuando te zumba el oido izquierdo.” Medications such as antidepressants or anti-anxiety drugs may be prescribed to address comorbid psychological conditions that exacerbate the auditory sensation. However, the use of medication is carefully evaluated, considering potential side effects and individual patient factors.
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
Cognitive behavioral therapy provides individuals with coping strategies to manage the emotional and psychological impact of the auditory sensation. CBT techniques help individuals challenge negative thought patterns, develop relaxation skills, and modify behaviors that contribute to the distress associated with “que es cuando te zumba el oido izquierdo.” This approach empowers individuals to regain control over their response to the auditory experience and improve their overall well-being.
- Lifestyle Modifications
Lifestyle modifications play a significant role in mitigating the effects of “que es cuando te zumba el oido izquierdo.” Reducing exposure to loud noise, managing stress levels, avoiding ototoxic substances (e.g., certain medications, excessive caffeine or alcohol), and maintaining a healthy diet and sleep schedule can all contribute to reducing the frequency and intensity of the auditory sensation.
In conclusion, the successful management and mitigation of “que es cuando te zumba el oido izquierdo” requires a personalized and integrated approach. Addressing underlying medical conditions, implementing audiological interventions, providing psychological support, and encouraging lifestyle modifications are essential components in improving the individual’s ability to cope with this auditory experience and enhance their overall quality of life. Regular monitoring and follow-up are necessary to ensure the effectiveness of management strategies and adjust interventions as needed.
7. Professional medical evaluation
The symptom “que es cuando te zumba el oido izquierdo” (the sensation of ringing, buzzing, or hissing in the left ear) necessitates a professional medical evaluation due to the potential for diverse underlying causes. This evaluation serves as a crucial step in differentiating between benign, transient occurrences and indicators of significant medical conditions. For example, persistent tinnitus could stem from noise-induced hearing loss, Meniere’s disease, acoustic neuroma, or even cardiovascular issues. A professional evaluation enables the identification of these underlying etiologies, guiding subsequent treatment strategies and preventing potential disease progression.
The evaluation typically encompasses a comprehensive medical history, physical examination, and specialized audiological testing. The medical history aims to identify potential risk factors, such as exposure to loud noise, medication use, or pre-existing medical conditions. The physical examination assesses the overall health status and identifies any visible abnormalities. Audiological testing evaluates hearing thresholds, assesses the function of the middle ear, and identifies the characteristics of the perceived auditory sensation. In some instances, further investigations, such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), may be warranted to rule out neurological causes. These evaluations provide a complete clinical picture.
In summary, the value of a professional medical evaluation in the context of “que es cuando te zumba el oido izquierdo” cannot be overstated. Early and accurate diagnosis facilitates targeted management strategies, alleviating the symptomatic burden and preventing the progression of underlying medical conditions. While the sensation might seem innocuous, it is important to seek expert medical advice to ensure that appropriate investigations are conducted and that optimal care is provided. Failing to pursue a professional evaluation could have serious implications if the root cause goes unchecked.
Frequently Asked Questions
The following questions address common concerns regarding the experience of auditory sensations, specifically ringing, buzzing, or hissing in the left ear.
Question 1: What are the potential causes of this auditory sensation?
The etiology can be diverse, ranging from noise-induced hearing loss and Meniere’s disease to medication side effects and neurological conditions such as acoustic neuroma. Stress and temporomandibular joint disorders may also contribute.
Question 2: When should a medical professional be consulted regarding this issue?
A consultation is warranted if the auditory sensation is persistent, severe, accompanied by other symptoms (e.g., dizziness, hearing loss), or significantly impacting daily life. A timely evaluation can help identify underlying causes and guide appropriate management.
Question 3: What types of tests are typically conducted during a medical evaluation for this condition?
A medical evaluation usually involves a comprehensive medical history, physical examination, and audiologic testing. Additional investigations, such as MRI or CT scans, may be necessary to rule out neurological or structural abnormalities.
Question 4: Can stress exacerbate the experience of left ear ringing?
Stress has been shown to exacerbate auditory sensations. Physiological responses to stress, such as increased muscle tension and elevated blood pressure, can amplify the perception of ringing or buzzing.
Question 5: What are some potential management strategies for this condition?
Management strategies vary depending on the underlying cause and may include hearing aids, tinnitus maskers, medication (e.g., anti-anxiety drugs), cognitive behavioral therapy, and lifestyle modifications (e.g., stress reduction, noise avoidance).
Question 6: Is there a cure for this auditory sensation?
A definitive cure may not always be possible, particularly if the underlying cause is chronic or irreversible. However, management strategies can often significantly reduce the impact of the auditory sensation on daily life and improve overall well-being.
These questions offer insight into the perception of auditory disturbances. The guidance highlights the significance of seeking prompt medical attention when persistent symptoms emerge. Additionally, it emphasized the importance of holistic methods in handling tinnitus and related illnesses.
The subsequent sections will detail various methods for managing stress to mitigate symptoms associated with these auditory perceptions.
Conclusion
The preceding exploration of “que es cuando te zumba el oido izquierdo” has illuminated the multifaceted nature of this auditory phenomenon. Key points include the variability of potential underlying causes, ranging from otological and neurological conditions to environmental and lifestyle factors. The importance of a thorough medical evaluation to determine the specific etiology was emphasized, along with the understanding that stress frequently acts as an exacerbating agent. A range of management strategies, including audiological interventions, pharmacological approaches, cognitive behavioral therapy, and lifestyle modifications, were discussed as methods to mitigate the impact on daily life.
Given the potential for “que es cuando te zumba el oido izquierdo” to significantly affect an individual’s well-being, proactive management and informed decision-making are essential. It is imperative that those experiencing persistent or concerning auditory sensations seek professional medical advice for accurate diagnosis and tailored treatment. Furthermore, continued research into the underlying mechanisms and effective interventions for this condition remains crucial to improve the quality of life for affected individuals.