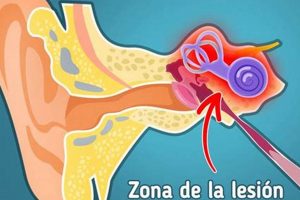
The sensation of ringing, buzzing, or hissing in the left ear, along with the query about its meaning, represents a common experience. Individuals often describe this auditory perception, experienced in the absence of an external sound source, as bothersome or concerning. The underlying reasons can be varied, ranging from simple and temporary causes to more complex medical conditions.
Understanding the possible origins of this auditory disturbance is beneficial for several reasons. It allows individuals to differentiate between transient occurrences and potential health issues that warrant medical attention. A deeper comprehension of potential causes promotes proactive health management and facilitates informed discussions with healthcare professionals. Historically, such phenomena were sometimes attributed to supernatural events; however, modern medicine provides a more scientific basis for understanding and addressing the issue.
Further exploration into the potential etiological factors, diagnostic approaches, and available treatments for this auditory phenomenon is warranted. The ensuing discussion will cover common reasons for its occurrence, methods used for identifying the underlying cause, and various strategies for managing the symptom.
Addressing Auditory Disturbances in the Left Ear
Managing the subjective experience of ringing, buzzing, or hissing localized to the left ear requires a multifaceted approach. The following recommendations are intended to provide guidance; however, they do not substitute for professional medical advice.
Tip 1: Obtain an Audiological Evaluation: A comprehensive hearing assessment performed by a qualified audiologist is essential to determine the presence and nature of any underlying hearing loss or auditory dysfunction. This evaluation will provide a baseline for future comparisons and inform subsequent management strategies.
Tip 2: Manage Cerumen Accumulation: Excessive earwax buildup can contribute to perceived auditory disturbances. Consult a healthcare professional regarding safe and effective cerumen removal techniques, as improper removal attempts can lead to further complications.
Tip 3: Control Blood Pressure: Hypertension can exacerbate tinnitus symptoms. Regular monitoring of blood pressure and adherence to prescribed antihypertensive medications, in consultation with a physician, are critical for overall health and potentially mitigating auditory perceptions.
Tip 4: Reduce Exposure to Loud Noises: Prolonged exposure to high-intensity sound levels can damage the delicate structures of the inner ear and worsen tinnitus. Employ appropriate hearing protection, such as earplugs or earmuffs, in noisy environments.
Tip 5: Limit Caffeine and Alcohol Intake: Certain substances, including caffeine and alcohol, can stimulate the auditory system and intensify tinnitus. Moderation or elimination of these substances may result in a reduction in perceived auditory disturbances.
Tip 6: Explore Sound Therapy Options: Masking devices or environmental sound generators can help to reduce the perception of tinnitus by providing background noise that distracts from the internal sound. A healthcare professional can recommend appropriate sound therapy devices.
Tip 7: Consider Stress Management Techniques: Stress and anxiety can exacerbate tinnitus. Relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing exercises, meditation, or yoga, may help to reduce stress levels and improve overall well-being, potentially mitigating tinnitus symptoms.
These recommendations represent a starting point for managing the subjective experience of auditory disturbances. Consistent implementation of these strategies, in conjunction with professional medical guidance, can improve quality of life.
The successful management of perceived auditory disturbances hinges upon accurate diagnosis and tailored treatment approaches. The subsequent section will address potential therapeutic interventions and long-term management strategies.
1. Potential Causes
The sensation of ringing, buzzing, or hissing in the left ear, prompts an investigation into potential underlying causes. Determining the etiology is crucial for effective management and alleviating concerns associated with the auditory perception.
- Cerumen Impaction
Excessive earwax accumulation in the external auditory canal can obstruct sound transmission and irritate the tympanic membrane, resulting in the perception of tinnitus. Individuals experiencing this condition may report a feeling of fullness or pressure in the affected ear alongside the auditory disturbance. Cerumen management performed by a healthcare professional typically resolves the symptom.
- Noise-Induced Hearing Loss
Exposure to high-intensity sound levels can damage the delicate hair cells in the inner ear, leading to permanent hearing loss and tinnitus. The auditory perception may manifest as a high-pitched ringing or buzzing. This form of hearing loss is often preventable through the consistent use of hearing protection in noisy environments.
- Meniere’s Disease
This inner ear disorder is characterized by episodic vertigo, hearing loss, tinnitus, and a feeling of fullness in the ear. The tinnitus associated with Meniere’s disease is often described as a low-frequency roaring or buzzing sound. The exact cause of Meniere’s disease remains unknown, and management focuses on controlling symptoms.
- Medications
Certain medications, including some antibiotics, anti-inflammatory drugs, and chemotherapy agents, are ototoxic and can cause tinnitus as a side effect. The onset of tinnitus following the initiation of a new medication should prompt a discussion with a healthcare provider to evaluate potential alternatives.
These causes represent a selection of potential etiologies for the perception of auditory disturbances localized to the left ear. The presence, intensity, and characteristics of the subjective sound should be assessed by a healthcare professional to determine the underlying cause and guide appropriate management strategies.
2. Audiological Assessment
An audiological assessment serves as a critical diagnostic tool in evaluating the subjective experience of auditory perception in the left ear. The sensation of ringing, buzzing, or hissing necessitates a comprehensive evaluation of the auditory system to determine the underlying cause and guide appropriate intervention strategies. This assessment extends beyond a simple hearing test; it involves a series of procedures designed to isolate specific auditory dysfunctions that may be contributing to the reported symptoms. For example, an individual reporting a consistent high-pitched tone in the left ear undergoes pure-tone audiometry to determine the presence and extent of any hearing loss at specific frequencies. This test helps to ascertain if the perceived sound aligns with actual deficits in auditory function.
Further elements of the audiological assessment include speech audiometry, which evaluates the ability to understand speech in quiet and noisy environments. Impedance audiometry assesses the function of the middle ear, identifying potential issues such as fluid accumulation or tympanic membrane perforations, which can indirectly affect auditory perception. Otoacoustic emissions (OAEs) testing measures the function of the outer hair cells in the cochlea, providing insight into the integrity of the inner ear. For instance, an individual with normal hearing thresholds but reduced OAEs may suggest cochlear dysfunction that contributes to the perception of sounds in the absence of external stimuli. Furthermore, auditory brainstem response (ABR) testing examines the neural pathways from the inner ear to the brainstem, identifying potential neurological factors impacting auditory processing. This is particularly relevant in cases where tinnitus is accompanied by other neurological symptoms.
In summary, audiological assessment is not merely a process of measuring hearing sensitivity. Rather, it serves as an indispensable tool for dissecting the auditory system, identifying potential contributing factors to subjective auditory perceptions, and directing appropriate management strategies. The objective data gathered through this assessment is essential for formulating a diagnosis, predicting the prognosis, and tailoring treatment interventions to address the specific needs of individuals experiencing auditory disturbances in the left ear.
3. Tinnitus Management
The subjective perception of sound in the left ear, often described as ringing, buzzing, or hissing, necessitates a comprehensive approach to tinnitus management. This auditory phenomenon, experienced in the absence of external stimuli, directly impacts an individual’s quality of life. Effective management strategies are essential for mitigating the distress associated with this condition. Consider an individual experiencing persistent, high-frequency ringing following exposure to loud machinery. Tinnitus management, in this instance, involves sound therapy to mask the unwanted noise, counseling to address the psychological impact, and potentially, hearing aids to compensate for any concurrent hearing loss. Each element contributes to reducing the individual’s awareness and negative reactions to the tinnitus.
Management techniques include, but are not limited to, sound therapy, cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT), and tinnitus retraining therapy (TRT). Sound therapy utilizes external sounds to mask or habituate the perception of tinnitus. CBT helps individuals to change negative thought patterns and emotional responses associated with the sound, while TRT combines counseling and sound therapy to promote habituation, enabling the brain to filter out the tinnitus signal. The selection of appropriate techniques depends on the individuals specific needs and the characteristics of the tinnitus. A musician, for example, may benefit from specialized hearing protection and sound enrichment strategies to prevent further auditory damage and manage existing symptoms.
Successful tinnitus management aims to reduce the perceived loudness and intrusiveness of the sound, improve sleep quality, and enhance overall well-being. A proactive and personalized approach, involving collaboration between audiologists, physicians, and mental health professionals, optimizes outcomes. Ignoring the sensation and hoping that it will disappear is not a viable strategy, and can lead to increased anxiety and decreased quality of life. Therefore, seeking professional guidance and actively engaging in tinnitus management is crucial for individuals experiencing auditory disturbances in the left ear.
4. Underlying Conditions
The subjective experience of auditory perception in the left ear, prompts an investigation into potential underlying medical conditions. Its presence may signal the existence of a broader health concern that requires diagnosis and treatment. The reported sensations should be evaluated in the context of overall health status.
- Cardiovascular Disease
Cardiovascular conditions, such as hypertension or atherosclerosis, can disrupt blood flow to the inner ear, potentially leading to auditory disturbances. Reduced circulation to the delicate structures of the cochlea may result in the perception of ringing or buzzing. Effective management of cardiovascular risk factors, including blood pressure control and cholesterol reduction, may influence the severity of auditory symptoms. For example, an individual with uncontrolled hypertension may experience a worsening of tinnitus during periods of elevated blood pressure.
- Thyroid Disorders
Thyroid dysfunction, whether hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism, can affect various bodily functions, including auditory processing. Hormonal imbalances may disrupt the neural pathways involved in hearing, resulting in the perception of sounds in the absence of external stimuli. Thyroid hormone replacement therapy, in the case of hypothyroidism, or management of hyperthyroidism, can impact auditory symptoms.
- Neurological Conditions
Certain neurological conditions, such as multiple sclerosis or acoustic neuroma, can affect the auditory nerve or brainstem, leading to auditory disturbances. Multiple sclerosis may disrupt the transmission of auditory signals, while an acoustic neuroma, a benign tumor on the auditory nerve, can compress the nerve and cause tinnitus or hearing loss. Diagnosis and management of neurological conditions often require specialized neurological evaluation and intervention.
- Temporomandibular Joint (TMJ) Disorders
Dysfunction of the temporomandibular joint can indirectly affect auditory perception due to the proximity of the TMJ to the ear. Muscle tension and inflammation in the TMJ region may radiate to the ear, causing tinnitus or a feeling of fullness. Management of TMJ disorders through physical therapy, medication, or dental appliances may alleviate related auditory symptoms.
The identified health conditions provide a glimpse into the diverse factors contributing to perceived sounds in the left ear. A comprehensive medical history, physical examination, and targeted diagnostic testing, are essential to establish an accurate diagnosis and guide appropriate treatment strategies. These conditions emphasize the interconnectedness of auditory health and overall well-being, highlighting the necessity for a holistic approach in managing such experiences.
5. Lifestyle Factors
Lifestyle factors significantly influence the perception and persistence of auditory disturbances localized to the left ear. These factors encompass various behavioral and environmental elements that, either independently or in combination, can exacerbate or mitigate subjective auditory sensations.
- Dietary Habits
Certain dietary components may influence the perception of auditory phenomena. High sodium intake can contribute to fluid retention, potentially affecting inner ear pressure and exacerbating symptoms. Conversely, deficiencies in essential nutrients, such as vitamin B12 or magnesium, have been linked to auditory dysfunction. Consistent and balanced nutrition is crucial for maintaining optimal auditory function.
- Smoking and Alcohol Consumption
Nicotine and alcohol impact the cardiovascular system, potentially reducing blood flow to the inner ear. Reduced circulation can compromise the health of auditory cells, increasing susceptibility to tinnitus. Both smoking and excessive alcohol intake have been associated with a higher incidence of perceived auditory disturbances. Abstinence or moderation is advised.
- Physical Activity
Regular physical activity promotes healthy circulation and reduces stress levels, potentially benefiting auditory health. Conversely, a sedentary lifestyle can contribute to cardiovascular issues and increased stress, exacerbating existing conditions. Engaging in moderate exercise promotes overall well-being, indirectly supporting auditory function.
- Stress Management
Chronic stress and anxiety elevate cortisol levels, which can negatively impact various bodily functions, including auditory processing. Stress management techniques, such as mindfulness meditation or yoga, promote relaxation and reduce the impact of stress on the auditory system. Effective stress management is essential for mitigating the perception of auditory disturbances.
These lifestyle factors, while seemingly disparate, converge to influence the delicate balance of the auditory system. Modifications to these elements can significantly impact the perception and persistence of sounds in the left ear. The adoption of a holistic approach to health, incorporating sound dietary choices, avoidance of harmful substances, regular physical activity, and effective stress management, offers a viable strategy for mitigating the impact of such disturbances.
6. Emotional Impact
The presence of persistent auditory perceptions localized to the left ear can elicit a range of emotional responses that significantly impact an individual’s psychological well-being. The chronic nature of the sensation, experienced in the absence of external stimuli, can lead to heightened stress, anxiety, and frustration.
- Increased Anxiety and Irritability
The persistent and often unpredictable nature of the sound can create heightened anxiety. Individuals may become hyper-vigilant, constantly monitoring for the sound, which can lead to increased stress levels and irritability. The inability to escape the perception of the auditory phenomenon can foster a sense of helplessness and unease. For instance, an individual might experience increased anxiety in quiet environments where the sound is more noticeable, disrupting concentration and increasing feelings of tension.
- Sleep Disturbances
The presence of the perceived sound can interfere with sleep patterns. The constant ringing, buzzing, or hissing may make it difficult to fall asleep or stay asleep, leading to chronic sleep deprivation. This, in turn, can exacerbate anxiety, depression, and cognitive impairment. An example is a situation where the auditory sensation intensifies at night, preventing restful sleep and causing daytime fatigue.
- Social Isolation and Withdrawal
Individuals may withdraw from social activities due to the discomfort and frustration associated with the auditory perception. The fear of being unable to hear conversations or the embarrassment of constantly asking people to repeat themselves can lead to social isolation. This social withdrawal can further exacerbate feelings of loneliness and depression. An individual might avoid attending social gatherings or noisy environments, limiting social interactions and leading to feelings of isolation.
- Depression and Feelings of Hopelessness
The chronic nature of the auditory phenomenon, coupled with the lack of a definitive cure, can lead to feelings of depression and hopelessness. The persistent sound can negatively impact mood, motivation, and overall quality of life. Individuals may experience a loss of interest in activities they once enjoyed, leading to a diminished sense of well-being. The constant struggle to cope with the sensation can contribute to feelings of despair and a belief that the condition is unmanageable.
The emotional impact of auditory perception localized to the left ear should not be underestimated. The chronic and disruptive nature of the sensation can have far-reaching consequences for an individual’s psychological well-being, highlighting the importance of comprehensive management strategies that address both the physical and emotional aspects of the condition.
Frequently Asked Questions Regarding Auditory Perception in the Left Ear
The following section addresses common queries pertaining to the sensation of ringing, buzzing, or hissing localized to the left ear. The information provided aims to clarify uncertainties and offer a deeper understanding of this auditory phenomenon.
Question 1: What are the primary causes?
The primary causes include cerumen impaction, noise-induced hearing loss, Meniere’s disease, certain medications, cardiovascular conditions, and temporomandibular joint disorders. A comprehensive medical evaluation is necessary to determine the specific underlying cause.
Question 2: Is this condition permanent?
The permanence of the subjective auditory sensation depends on the underlying cause. In some cases, such as those related to temporary noise exposure or cerumen impaction, the symptom may resolve with treatment. However, in cases involving chronic conditions like Meniere’s disease or noise-induced hearing loss, the condition may persist.
Question 3: When should a healthcare professional be consulted?
A healthcare professional should be consulted if the auditory perception is persistent, interferes with daily activities, is accompanied by other symptoms such as dizziness or hearing loss, or develops suddenly. Prompt evaluation can facilitate timely diagnosis and management.
Question 4: What diagnostic tests are typically performed?
Typical diagnostic tests include otoscopy to examine the ear canal, audiometry to assess hearing thresholds, tympanometry to evaluate middle ear function, and potentially, imaging studies such as MRI to rule out structural abnormalities.
Question 5: What management strategies are available?
Management strategies depend on the underlying cause. Options may include cerumen removal, hearing aids, sound therapy, cognitive behavioral therapy, medication for underlying medical conditions, and lifestyle modifications such as reducing exposure to loud noises and managing stress.
Question 6: Can lifestyle changes influence this condition?
Lifestyle changes can influence the condition. Reducing sodium intake, avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption, managing stress, engaging in regular physical activity, and maintaining adequate hydration may alleviate symptoms.
These responses provide a foundational understanding of auditory sensations localized to the left ear. Seeking personalized medical advice is crucial for accurate diagnosis and effective management.
The information presented offers a comprehensive overview of various aspects related to this specific health concern. Further exploration can be achieved through detailed medical consultations.
Conclusion
The inquiry “me zumba el oido izquierdo que significa” initiates an exploration into the subjective experience of auditory perceptions localized to the left ear. This discussion has encompassed potential etiological factors, diagnostic methodologies, and available management strategies. Conditions such as cerumen impaction, noise-induced hearing loss, and underlying medical conditions, alongside lifestyle and emotional factors, contribute to the complexity of this phenomenon.
The manifestation warrants serious consideration and comprehensive evaluation. Proactive engagement with healthcare professionals is paramount for accurate diagnosis and the implementation of tailored management plans. Continued research and advancements in audiological care offer the prospect of improved understanding and enhanced interventions for individuals experiencing auditory disturbances.