The sensation of ringing in the right ear, commonly described as a buzzing or humming sound, is a frequent experience for many individuals. This phenomenon, often transient, can manifest in various forms and intensities. It is generally understood as a form of tinnitus, the perception of sound when no external auditory stimulus is present. As an example, someone might suddenly perceive a high-pitched tone solely in their right ear, which may fade away within minutes or persist for a longer duration.
Understanding the possible causes of this auditory experience is important for appropriate management and potential relief. While often benign and self-limiting, persistent or recurring instances may warrant further investigation to rule out underlying medical conditions. Historically, such sensations have been attributed to diverse superstitious beliefs, but modern medical science offers more concrete explanations rooted in physiological and neurological processes.
The following discussion will explore the common causes of right ear ringing, differentiate between transient and chronic cases, and outline potential diagnostic approaches and treatment options available to those experiencing this phenomenon.
Addressing Ringing in the Right Ear
When experiencing a buzzing or ringing sensation in the right ear, several steps can be taken to understand and potentially alleviate the issue.
Tip 1: Monitor Frequency and Duration: Observe how often the ringing occurs and how long it lasts. A log can help identify patterns or triggers.
Tip 2: Review Medication List: Certain medications are known to cause tinnitus as a side effect. Consult with a physician or pharmacist to determine if any current medications may be contributing to the sensation.
Tip 3: Assess Noise Exposure: Evaluate recent exposure to loud noises. Prolonged or intense noise can temporarily or permanently damage hearing, leading to tinnitus. Consider using ear protection in noisy environments.
Tip 4: Manage Stress Levels: Stress and anxiety can exacerbate tinnitus. Incorporate stress-reduction techniques such as exercise, meditation, or deep breathing exercises.
Tip 5: Limit Caffeine and Alcohol Intake: These substances can affect blood flow and potentially worsen tinnitus symptoms in some individuals.
Tip 6: Seek Professional Evaluation: If the ringing persists or is accompanied by other symptoms such as hearing loss, dizziness, or ear pain, consult an audiologist or physician for a comprehensive evaluation.
Addressing the sensation involves careful observation, lifestyle adjustments, and professional consultation when necessary. Early intervention can often mitigate the impact on quality of life.
The following section will delve into the potential medical causes and treatment options for persistent right ear ringing.
1. Tinnitus perception
Tinnitus perception represents the subjective auditory experience of sound in the absence of an external source, a phenomenon directly relevant to the query “que significa cuando el oido derecho te zumba” (what does it mean when your right ear is ringing). The ringing or buzzing sensation, in this context, is the tinnitus perception. This perception can vary widely in pitch, loudness, and character, ranging from a high-pitched whine to a low-frequency hum, and can be constant or intermittent. The “que significa cuando el oido derecho te zumba” question arises specifically because of this individual’s internal perception of sound.
The specific localization of the tinnitus to the right ear is significant. While tinnitus can be bilateral, unilateral tinnitus, particularly if new or accompanied by other symptoms, warrants careful evaluation. For instance, a person experiencing a sudden onset of ringing exclusively in their right ear after a head injury may have a different underlying cause than someone with gradual, bilateral tinnitus related to age-related hearing loss. Understanding the perception (sound quality, location, duration) is therefore a crucial first step in understanding “que significa cuando el oido derecho te zumba”. The quality of one’s perception is based solely in the individual’s mind.
In summary, the phrase “que significa cuando el oido derecho te zumba” inherently references the tinnitus perception. Differentiating the individual’s experience (the perceived sound) from its potential causes is essential for accurate diagnosis and management. The nature and location of the tinnitus are critical details guiding the diagnostic process, ultimately determining the answer to “que significa cuando el oido derecho te zumba” for that specific individual.
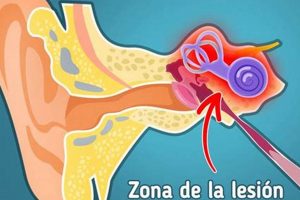
2. Auditory system function
The functionality of the auditory system is intrinsically linked to the perception described in “que significa cuando el oido derecho te zumba” (what does it mean when your right ear is ringing). The integrity and proper operation of the various components of this system directly influence whether and how sounds, real or perceived, are registered and interpreted.
- Outer Ear and Sound Transmission
The outer ear, including the ear canal, collects and funnels sound waves towards the eardrum. Impairment in this area, such as blockage from earwax or infection, can alter sound conduction and potentially contribute to the perception of tinnitus. For instance, a build-up of cerumen in the right ear could amplify internal body sounds, manifesting as a ringing or buzzing, thereby influencing “que significa cuando el oido derecho te zumba”.
- Middle Ear Mechanics
The middle ear houses the ossicles (tiny bones) that amplify and transmit vibrations to the inner ear. Conditions affecting the ossicles, such as otosclerosis (abnormal bone growth), can disrupt this process and generate abnormal signals that the brain interprets as sound. Stiffening of these bones specifically in the right ear may cause the sensation described in “que significa cuando el oido derecho te zumba”.
- Inner Ear and Cochlear Function
The inner ear, particularly the cochlea, contains hair cells that transduce vibrations into electrical signals sent to the brain. Damage to these hair cells, often due to noise exposure or age-related degeneration, is a common cause of tinnitus. Selective damage to hair cells in the right cochlea can lead to the unilateral ringing described by “que significa cuando el oido derecho te zumba”.
- Auditory Nerve and Brain Processing
The auditory nerve carries signals from the inner ear to the brain, where they are processed and interpreted as sound. Issues affecting the nerve, such as acoustic neuroma (a benign tumor), or abnormalities in brain processing can also contribute to tinnitus. Aberrant neural activity along the right auditory pathway might be perceived as the phantom sound described in “que significa cuando el oido derecho te zumba”.
In summary, the question “que significa cuando el oido derecho te zumba” necessitates an understanding of the auditory system’s complex functions. Any disruption along this pathway, from the outer ear to the brain, can contribute to the perception of tinnitus. Comprehensive evaluation often involves assessing each component of the auditory system to pinpoint the source of the aberrant signals underlying the sensation of ringing.
3. Possible underlying causes
Identifying potential etiological factors is paramount in determining “que significa cuando el oido derecho te zumba” (what does it mean when your right ear is ringing). A comprehensive evaluation of possible underlying causes is crucial for appropriate diagnosis and management of this auditory perception.
- Noise-Induced Hearing Loss
Exposure to loud noises, either acute or chronic, can damage the hair cells within the cochlea, leading to tinnitus. The specific impact on the right ear, as described in “que significa cuando el oido derecho te zumba”, may result from asymmetrical noise exposure or pre-existing vulnerabilities in that ear. For example, a construction worker consistently exposed to loud machinery on their right side might experience ringing primarily in the right ear due to selective damage.
- Medications
Certain medications are ototoxic, meaning they can damage the inner ear and cause tinnitus. Aspirin, NSAIDs, certain antibiotics, and chemotherapy drugs are among the medications with known ototoxic effects. The onset of ringing in the right ear, as queried in “que significa cuando el oido derecho te zumba”, may correlate with the initiation or dosage change of such a medication. Discontinuing the medication, under medical supervision, may resolve the tinnitus.
- Meniere’s Disease
Meniere’s disease is an inner ear disorder characterized by episodes of vertigo, hearing loss, tinnitus, and a feeling of fullness in the ear. While Meniere’s disease can affect both ears, it often presents unilaterally. If the right ear is affected, the resulting tinnitus, described as “que significa cuando el oido derecho te zumba”, can be a prominent symptom, accompanied by the aforementioned symptoms.
- Temporomandibular Joint (TMJ) Disorders
Dysfunction of the temporomandibular joint, which connects the jaw to the skull, can sometimes lead to tinnitus. The close proximity of the TMJ to the ear means that TMJ disorders can affect structures within the ear, potentially resulting in the sensation described by “que significa cuando el oido derecho te zumba”. Muscle tension and nerve irritation associated with TMJ dysfunction may manifest as ringing, particularly if the TMJ dysfunction is more pronounced on the right side.
In conclusion, understanding “que significa cuando el oido derecho te zumba” necessitates a thorough exploration of potential underlying causes. Noise exposure, medications, inner ear disorders, and TMJ dysfunction represent only a subset of the factors that can contribute to this symptom. A detailed medical history, physical examination, and audiological testing are essential to identify the specific etiology and guide appropriate management strategies.
4. Diagnostic evaluation
The perception of ringing in the right ear, the phenomenon described as “que significa cuando el oido derecho te zumba,” necessitates a comprehensive diagnostic evaluation to determine the underlying cause. This evaluation is a systematic process designed to identify potential factors contributing to the auditory sensation. Without a thorough assessment, management strategies remain speculative and potentially ineffective. The relationship is direct: “que significa cuando el oido derecho te zumba” prompts the need for diagnostic procedures, and the findings of those procedures inform the understanding of “que significa cuando el oido derecho te zumba.” For instance, if an individual reports ringing in their right ear, an initial evaluation may involve examining the ear canal for obstructions or signs of infection. If those are ruled out, further investigation into hearing sensitivity and middle ear function will be performed.
The diagnostic process typically includes several components. First, a detailed medical history is obtained, inquiring about noise exposure, medication use, and any pre-existing medical conditions. Second, a physical examination is performed, focusing on the ear, head, and neck. Third, audiological testing is conducted to assess hearing sensitivity, speech discrimination, and the presence of tinnitus. These tests may include pure-tone audiometry, tympanometry, and otoacoustic emissions testing. The specific tests employed are guided by the initial findings and the clinical suspicion of potential underlying causes. As an example, if the audiological evaluation reveals unilateral hearing loss concurrent with the right ear ringing, imaging studies, such as MRI, may be ordered to rule out an acoustic neuroma.
The outcome of the diagnostic evaluation directly influences the interpretation of “que significa cuando el oido derecho te zumba” and guides subsequent management strategies. Challenges arise when the evaluation fails to identify a clear etiology, in which case, the tinnitus is classified as idiopathic. Even in these cases, the diagnostic process serves to exclude potentially serious underlying conditions, offering reassurance and informing the development of coping strategies. The integration of subjective reporting (“que significa cuando el oido derecho te zumba”) with objective diagnostic findings is critical for effective patient care.
5. Management strategies
The effectiveness of any management strategy for right ear ringing, intrinsically linked to “que significa cuando el oido derecho te zumba,” hinges on accurately identifying the underlying cause. If the ringing stems from noise exposure, protective measures such as earplugs or noise-canceling headphones are indicated. For medication-induced tinnitus, consulting with a physician about alternative drugs or dosage adjustments is critical. If Meniere’s disease is diagnosed, dietary modifications, medications to control vertigo, or, in severe cases, surgical interventions may be considered. TMJ-related tinnitus might benefit from physical therapy, mouth guards, or dental interventions aimed at correcting jaw alignment. In essence, the management strategy directly addresses the identified etiology impacting the subjective perception described as “que significa cuando el oido derecho te zumba.”
When a specific cause remains elusive despite comprehensive evaluation (idiopathic tinnitus), management shifts towards mitigating the distress associated with the ringing. Sound therapy, involving the use of white noise generators or tinnitus maskers, can reduce the perceived loudness of the tinnitus and provide relief. Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) can assist individuals in managing the psychological impact of tinnitus, teaching coping mechanisms to reduce anxiety and improve quality of life. Tinnitus retraining therapy (TRT) combines sound therapy with counseling to habituate the brain to the tinnitus signal, gradually reducing its perceived importance. These strategies acknowledge that the ringing may persist, but aim to minimize its interference with daily life, thereby modulating the individual’s interpretation of “que significa cuando el oido derecho te zumba.” For instance, a person experiencing persistent right ear ringing despite negative diagnostic findings could utilize a bedside sound machine playing nature sounds to facilitate sleep, thereby addressing the practical challenge of insomnia caused by the tinnitus.
Successful management of “que significa cuando el oido derecho te zumba” ultimately relies on a personalized approach. The initial diagnostic evaluation, identification of underlying causes (where possible), and implementation of tailored strategies form an iterative process. Challenges arise from the subjective nature of tinnitus perception and the complexity of the auditory system. However, a collaborative approach between the individual experiencing the ringing and healthcare professionals, including audiologists and physicians, can optimize outcomes and significantly improve the individual’s ability to live with and manage the sensation. Understanding “que significa cuando el oido derecho te zumba” is, therefore, not merely a search for a cure, but a process of understanding, adapting, and managing a persistent auditory sensation.
Frequently Asked Questions Regarding Right Ear Ringing
This section addresses common inquiries regarding the phenomenon of ringing in the right ear, providing concise and factual information.
Question 1: What are the most common causes of ringing specifically in the right ear?
Ringing in the right ear can stem from various factors, including noise exposure affecting the right ear more significantly than the left, medication side effects, temporomandibular joint (TMJ) disorders impacting the right side, and, less commonly, specific neurological conditions. It is crucial to note that idiopathic tinnitus, where the cause cannot be determined, is also possible.
Question 2: When should one seek medical attention for ringing in the right ear?
Medical consultation is warranted if the ringing is sudden in onset, persistent, accompanied by hearing loss, dizziness, ear pain, or any other neurological symptoms. The sudden occurrence or presence of associated symptoms necessitates prompt evaluation to rule out potentially serious underlying conditions.
Question 3: Can stress or anxiety cause ringing in the right ear?
While stress and anxiety do not directly cause tinnitus, they can exacerbate existing tinnitus or make the perception more noticeable. Management of stress and anxiety can improve the overall quality of life for individuals experiencing ringing in the ear, but does not address the physiological origin of the sound.
Question 4: Is there a cure for ringing in the right ear?
A definitive cure for tinnitus remains elusive, particularly for idiopathic cases. However, numerous management strategies can reduce the impact of tinnitus on daily life. When the underlying cause is treatable, such as an ear infection or medication side effect, addressing that cause may resolve the ringing.
Question 5: What are some self-care strategies that can help manage ringing in the right ear?
Self-care strategies include avoiding excessive noise exposure, managing stress levels, limiting caffeine and alcohol intake, ensuring adequate sleep, and using white noise generators to mask the tinnitus. These strategies provide symptomatic relief but do not address the root cause.
Question 6: Can earwax buildup cause ringing in the right ear?
Yes, earwax buildup can indeed cause ringing in the right ear. The impaction of cerumen against the eardrum can alter its vibratory properties, leading to the perception of sound in the absence of an external stimulus. A healthcare professional can safely remove the earwax, potentially resolving the tinnitus.
Accurate diagnosis and personalized management are vital for individuals experiencing ringing in the right ear. The provided answers highlight common concerns and offer guidance on addressing this auditory phenomenon.
Further information on the diagnosis and treatment of right ear ringing can be found in the following section.
Understanding the Significance of Right Ear Ringing
The exploration of “que significa cuando el oido derecho te zumba” has underscored the multifaceted nature of this auditory perception. The discussion encompassed potential etiologies, diagnostic approaches, and management strategies, reflecting the complexity inherent in the subjective experience of tinnitus. It is essential to recognize that right ear ringing is not merely a symptom but potentially indicative of underlying physiological or neurological processes. A comprehensive evaluation, guided by a detailed history and clinical examination, is crucial for accurate diagnosis and effective intervention.
The information presented serves to empower individuals experiencing this phenomenon to seek appropriate medical attention and engage in informed decision-making regarding their healthcare. Persistent or concerning right ear ringing should not be dismissed as trivial. Early identification of potential underlying causes and proactive management strategies are paramount for mitigating the impact on quality of life. Further research into the neurophysiological mechanisms of tinnitus and the development of targeted therapies remain critical areas of focus. The experience of “que significa cuando el oido derecho te zumba” warrants both individual attention and continued scientific investigation.