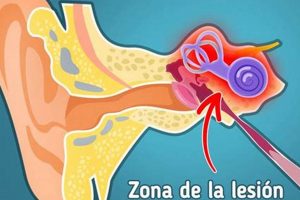
The sensation of ringing, buzzing, or other sounds in the right ear, absent of an external auditory stimulus, is a common query. Individuals experiencing this phenomenon often seek clarification regarding the potential causes and implications of this auditory perception.
The significance of understanding the source of this auditory disturbance lies in its potential impact on quality of life. Persistent occurrences may indicate underlying medical conditions requiring evaluation and management. Historically, such symptoms have been attributed to various factors ranging from minor earwax accumulation to more serious neurological issues.
The following sections will address the potential origins of this auditory symptom, diagnostic approaches, and available treatment options. Consideration will be given to both common and less frequent etiologies, enabling a more comprehensive understanding of the issue.
Considerations for Right Ear Tinnitus
Addressing the perception of sounds in the right ear requires a systematic approach. The following guidelines offer direction in understanding and managing this symptom.
Tip 1: Monitor Symptom Characteristics: Note the specific qualities of the sound, such as its pitch, loudness, and whether it is constant or intermittent. Detailed observation can assist in identifying patterns and potential triggers.
Tip 2: Review Medication List: Certain medications are known to have ototoxic effects. Consult a physician or pharmacist to determine if any prescribed or over-the-counter drugs could be contributing to the auditory symptom.
Tip 3: Evaluate Environmental Noise Exposure: Prolonged exposure to loud noises can damage the auditory system. Evaluate occupational and recreational activities for potential noise hazards and implement appropriate hearing protection measures.
Tip 4: Manage Stress Levels: Stress and anxiety can exacerbate tinnitus. Implement stress-reduction techniques such as mindfulness, meditation, or regular exercise.
Tip 5: Address Underlying Medical Conditions: Conditions such as hypertension, cardiovascular disease, and thyroid disorders can contribute to tinnitus. Ensure appropriate management of any pre-existing medical conditions.
Tip 6: Seek Professional Evaluation: If the symptom persists or worsens, consult an audiologist or otolaryngologist. Diagnostic testing can help identify the underlying cause and guide appropriate treatment.
Tip 7: Explore Sound Therapy Options: Techniques such as white noise machines or tinnitus retraining therapy can help mask or habituate to the unwanted sound.
Adherence to these suggestions offers a structured framework for evaluating and potentially alleviating the experience. Proactive monitoring and management can lead to improved outcomes.
The succeeding sections will delve into treatment methodologies and preventative strategies.
1. Auditory Perception
Auditory perception, the brain’s interpretation of sound waves, is central to understanding the sensation described as “porque me zumba el oido derecho que significa.” This sensation reflects an abnormality in the auditory processing pathway, leading to the perception of sound in the absence of an external stimulus.
- Neural Pathways and Signal Processing
Auditory perception begins with the transduction of sound waves into electrical signals by the inner ear. These signals travel along auditory nerves to the brainstem, midbrain, and ultimately the auditory cortex. Disruption at any point along these pathways can result in aberrant auditory perception. In the context of “porque me zumba el oido derecho que significa,” this may involve damaged hair cells in the right cochlea or neural misfiring along the right auditory nerve. This explains why the sensation is localized to the right ear.
- Central Auditory Processing Disorders (CAPD)
CAPD refers to deficits in the brain’s ability to process auditory information, even when hearing sensitivity is normal. While less frequently associated with localized sensations, CAPD can influence the perception of auditory distortions or phantom sounds. If the ringing or buzzing is perceived as complex or modulated, a central processing component should be considered. CAPD can alter the interpretation of otherwise normal auditory signals.
- Influence of Cognitive Factors
Auditory perception is not solely a sensory process; it is influenced by cognitive factors such as attention, expectation, and emotional state. For example, stress or anxiety can heighten awareness of pre-existing, but normally unnoticed, auditory activity. This explains why the described auditory sensation may fluctuate in intensity or frequency depending on the individual’s psychological state. Focused attention on the “zumbido” can amplify its perceived loudness and distress.
- Auditory Hallucinations
In rare cases, the reported sensation may represent an auditory hallucination. Auditory hallucinations involve perceiving sounds that originate entirely within the brain, often linked to neurological or psychiatric conditions. It is essential to differentiate this from tinnitus by considering the sound’s complexity and the presence of other neurological or psychological symptoms. Unlike typical tinnitus, auditory hallucinations may involve distinct voices or music.
These facets of auditory perception illustrate the complexity involved in understanding and diagnosing the sensation described. Pinpointing the source of the aberrant auditory perception, whether peripheral or central, and accounting for contributing cognitive factors, allows for targeted assessment and intervention related to “porque me zumba el oido derecho que significa.”
2. Potential etiology
Understanding the possible causes of the auditory sensation expressed as “porque me zumba el oido derecho que significa” is paramount for accurate diagnosis and effective management. Identifying the etiology requires consideration of a wide range of factors impacting auditory function in the right ear.
- Cerumen Impaction
Accumulation of earwax in the external auditory canal can obstruct sound transmission and create pressure on the tympanic membrane. This pressure can manifest as a buzzing or ringing sensation in the affected ear. Examination of the ear canal using an otoscope can confirm the presence of cerumen impaction. Prompt removal of the wax may resolve the auditory symptom. Failure to address impaction can lead to conductive hearing loss and exacerbate existing tinnitus.
- Noise-Induced Hearing Loss
Exposure to excessive noise levels damages the hair cells within the cochlea, the inner ear structure responsible for sound transduction. Damage to the hair cells in the right cochlea, specifically, can trigger a subjective buzzing or ringing perceived in the right ear. The degree of hearing loss and the perceived loudness of the tinnitus can vary depending on the extent of the damage. Avoiding further noise exposure and utilizing hearing protection are crucial to prevent further auditory damage.
- Meniere’s Disease
Meniere’s disease is an inner ear disorder characterized by episodes of vertigo, tinnitus, hearing loss, and a sensation of fullness in the affected ear. While Meniere’s disease can affect either ear, unilateral symptoms are common. The episodic nature of the symptoms, along with the presence of vertigo, distinguishes Meniere’s disease from other potential causes of tinnitus. Management typically involves dietary modifications, medication, and, in some cases, surgical intervention.
- Temporomandibular Joint (TMJ) Disorders
Dysfunction of the temporomandibular joint, located near the ear, can sometimes cause referred pain and auditory symptoms, including tinnitus. Misalignment of the jaw or muscle tension in the face and neck can affect the structures surrounding the ear, leading to a subjective sensation of buzzing or ringing. Treatment for TMJ disorders may involve physical therapy, bite guards, or medication to alleviate muscle tension and reduce inflammation.
These potential etiologies illustrate the complex interplay of factors that can contribute to the auditory sensation described. The individual’s medical history, audiological examination, and response to treatment guide the differentiation between these and other possible causes. Accurate identification of the underlying etiology informs targeted management strategies and improves the likelihood of symptom relief regarding “porque me zumba el oido derecho que significa”.
3. Subjective experience
The perception of a sound in the right ear, commonly described by the inquiry “porque me zumba el oido derecho que significa,” is fundamentally a subjective experience. Its manifestation and interpretation are unique to the individual, influencing the diagnostic process and potential treatment strategies. Recognizing the multifaceted nature of this subjectivity is crucial for comprehensive assessment.
- Individual Threshold of Awareness
The threshold at which an individual becomes aware of an internal auditory stimulus varies significantly. What might be an insignificant background noise for one person could be a source of considerable distress for another. Factors such as pre-existing anxiety, stress levels, and overall health can lower the threshold, making the sound more noticeable and bothersome. This highlights the necessity for tailored assessments that acknowledge each persons unique sensitivity.
- Descriptive Language and Interpretation
The way individuals describe the perceived sound differs substantially. The “zumbido” or buzzing sensation can be categorized using various terms like ringing, hissing, clicking, or roaring. The specific descriptive language used often influences the direction of diagnostic inquiry and may provide clues about the potential underlying mechanism. For example, a pulsating sound could suggest vascular involvement, whereas a high-pitched ringing is frequently associated with noise-induced hearing loss.
- Emotional and Psychological Impact
The psychological consequences of persistent auditory sensations significantly impact an individual’s overall well-being. Some experience mild annoyance, while others suffer from significant anxiety, depression, or sleep disturbances. The emotional response can amplify the perception of the sound, creating a feedback loop that perpetuates the distress. Assessing the psychological impact is essential for determining appropriate treatment strategies, which might include cognitive behavioral therapy or other psychological interventions.
- Coping Mechanisms and Adaptation
Individuals develop diverse strategies to cope with the auditory sensation, ranging from active sound masking to passive acceptance. The effectiveness of these coping mechanisms influences the overall impact on daily life. Some individuals find relief through white noise generators or background music, while others adapt by learning to ignore the sound through habituation techniques. Understanding these individual coping mechanisms can inform tailored management plans aimed at improving quality of life.
These facets underscore that addressing “porque me zumba el oido derecho que significa” requires a holistic approach that considers the personal experience of the auditory sensation. The subjective nature of the condition necessitates individualized assessment and treatment strategies to mitigate the impact and improve the individual’s overall well-being.
4. Possible tinnitus
The phrase “porque me zumba el oido derecho que significa” translates to “why is my right ear ringing, what does it mean?” The potential diagnosis of tinnitus directly addresses the core concern within this question. Tinnitus is the perception of sound when no external sound is present. As a primary cause, it explains the auditory phenomenon being experienced. The localized aspect, namely the right ear, indicates the potential for a specific source or pathway contributing to this perception, be it within the ear itself or along the related neurological pathways. The importance of considering tinnitus resides in its prevalence and range of underlying causes, from benign to potentially serious.
Identifying “possible tinnitus” as a component of “porque me zumba el oido derecho que significa” mandates a thorough audiological evaluation. This evaluation serves to rule out other causes and characterize the nature of the perceived sound. Examples of real-life scenarios include noise-induced hearing damage, which frequently presents as tinnitus, and age-related hearing loss, where tinnitus may become more noticeable as auditory acuity diminishes. Furthermore, systemic conditions such as hypertension or certain medications can contribute to or exacerbate tinnitus. The practical significance of understanding this connection is to initiate appropriate investigation and management, thereby addressing both the symptom and its potential underlying cause. Accurate diagnosis allows for targeted intervention, which may range from sound therapy to medication adjustments.
In summary, the query centers on an auditory symptom, and “possible tinnitus” represents a fundamental potential explanation. Recognizing this connection is crucial for prompting appropriate medical assessment and devising a personalized management strategy. Challenges may arise in differentiating between various forms of tinnitus and identifying its root cause, necessitating a comprehensive approach. The resolution to the initial question”porque me zumba el oido derecho que significa”lies in the accurate evaluation and management of possible tinnitus and the underlying factors contributing to its presentation.
5. Right ear specific
The inquiry, “porque me zumba el oido derecho que significa,” inherently focuses on a unilateral auditory experience. This specificity to the right ear necessitates exploration of factors that may be localized or disproportionately affecting that auditory system. Consideration must be given to anatomical, physiological, and pathological processes that could manifest primarily or exclusively in the right ear.
- Anatomical Asymmetries
Minor anatomical variations between the left and right auditory systems exist. These asymmetries, while often subtle, can influence susceptibility to certain conditions. For example, variations in the Eustachian tube’s angle or efficiency may predispose the right ear to pressure imbalances or infections, which could contribute to a ringing sensation. Consequently, imaging studies may be warranted to investigate structural differences that could explain the unilateral symptom.
- Vascular Abnormalities
Vascular structures supplying the inner ear may exhibit asymmetries or localized abnormalities. Pulsatile tinnitus, characterized by a rhythmic sound synchronized with the heartbeat, can arise from vascular anomalies such as arteriovenous malformations or carotid artery stenosis affecting the right side. Detailed vascular imaging, such as MRA or CTA, may be necessary to identify and characterize such vascular etiologies. The “right ear specific” localization warrants focused assessment of ipsilateral vascular structures.
- Unilateral Noise Exposure
While noise-induced hearing loss often affects both ears, asymmetrical exposure can occur. Certain occupational or recreational activities may preferentially expose the right ear to higher sound levels. Examples include operating machinery positioned predominantly on the right side or consistently using a mobile phone against the right ear. A detailed history of noise exposure, considering both intensity and laterality, is essential to determine if unilateral noise damage could be contributing to the reported symptom.
- Neurological Considerations
Lesions or abnormalities affecting the right auditory nerve or auditory cortex can manifest as unilateral auditory phenomena. Acoustic neuromas, benign tumors arising from the vestibulocochlear nerve, typically present with unilateral hearing loss, tinnitus, and vertigo. Similarly, cortical lesions affecting the right auditory cortex can result in auditory hallucinations or distorted sound perception localized to the contralateral ear. Neurological examination and imaging studies, such as MRI, are crucial to rule out these potential causes when the symptom is strictly unilateral.
The “right ear specific” attribute of the auditory complaint in “porque me zumba el oido derecho que significa” directs diagnostic efforts towards identifying localized factors influencing the right auditory system. By systematically evaluating anatomical variations, vascular structures, exposure patterns, and neurological integrity, clinicians can effectively narrow the differential diagnosis and implement targeted management strategies.
6. Symptom duration
The temporal aspect of an auditory disturbance, denoted as symptom duration, assumes critical importance in the clinical evaluation of “porque me zumba el oido derecho que significa.” Whether the symptom is transient, intermittent, or persistent significantly alters the diagnostic approach and management strategies.
- Acute Onset (Less than 72 hours)
The sudden appearance of a ringing sensation in the right ear necessitates immediate consideration of specific etiologies. Examples include acute acoustic trauma resulting from sudden exposure to loud noise, sudden idiopathic sensorineural hearing loss affecting the right ear, or ototoxic medication exposure. Rapid evaluation is crucial to identify potentially reversible causes and implement timely interventions. Delayed assessment may diminish the likelihood of successful treatment, particularly in cases of sudden hearing loss.
- Subacute Presentation (Days to Weeks)
A subacute onset, developing over days to weeks, suggests a different set of potential underlying factors compared to acute or chronic presentations. Inflammatory processes within the middle or inner ear, such as otitis media or labyrinthitis affecting the right ear, may manifest in this timeframe. Additionally, gradual changes in medication dosages or exposure to moderate levels of environmental noise may also contribute. Detailed review of recent medical history and environmental exposures is essential for diagnosis.
- Chronic Persistent (More than 3 Months)
Chronic, persistent tinnitus, lasting for over three months, often indicates more established underlying conditions. These conditions may include chronic noise-induced hearing loss, Meniere’s disease affecting the right ear, or age-related hearing loss. The management focus typically shifts from reversing the underlying cause to habituation and symptom management strategies. The extended duration can lead to significant psychological distress, warranting assessment and treatment for anxiety or depression.
- Intermittent Presentation (Episodic)
An episodic pattern, where the ringing in the right ear occurs sporadically with symptom-free intervals, requires consideration of fluctuating conditions. These conditions may include temporomandibular joint (TMJ) dysfunction, Eustachian tube dysfunction affecting the right ear, or vascular abnormalities causing transient auditory symptoms. Careful documentation of triggering factors and associated symptoms is essential for identifying the episodic nature and guiding management efforts.
Considering the symptom duration is crucial for differentiating between potential etiologies of “porque me zumba el oido derecho que significa”. Accurate assessment of the temporal profile assists in prioritizing diagnostic investigations and directing appropriate treatment pathways, from acute interventions to chronic management strategies.
7. Impact assessment
The assessment of impact is a critical component in the evaluation of the subjective auditory experience described in the question “porque me zumba el oido derecho que significa”. The perceived disturbances effect on an individual’s quality of life determines the urgency and intensity of diagnostic and therapeutic interventions. A minimal auditory sensation might be considered insignificant by one individual, while another might experience severe disruption due to the same stimulus, affecting daily activities and overall well-being.
For example, a musician experiencing ringing in the right ear, even at a low intensity, could be severely impacted due to the potential threat to their professional capacity. Conversely, an office worker might be less affected unless the symptom interferes with concentration or communication. Furthermore, the impact can extend beyond immediate functionality. The constant ringing may lead to sleep disturbances, anxiety, and even depression, all of which contribute to a diminished quality of life. Objective measures, such as tinnitus questionnaires and psychoacoustic assessments, can quantify the subjective experience and its broader implications on psychological health.
Understanding the impact of “porque me zumba el oido derecho que significa” allows for personalized treatment strategies that extend beyond simple audiological interventions. Addressing the psychological distress and functional limitations arising from the auditory sensation becomes paramount. Therefore, impact assessment serves not only to gauge the severity of the symptom but also to guide holistic management encompassing audiological, psychological, and lifestyle adjustments. Failure to adequately assess the impact may result in ineffective treatment focused solely on the auditory sensation, neglecting the significant psychological and functional consequences.
Frequently Asked Questions about Ringing in the Right Ear
The following questions address common concerns related to the sensation of sound, specifically ringing or buzzing, in the right ear. Information is provided to enhance understanding and guide appropriate action.
Question 1: What are the most common reasons for the perception of ringing specifically in the right ear?
The primary causes range from earwax buildup and noise-induced hearing loss to more complex conditions like Meniere’s disease or vascular issues. Specific medications can also trigger such sensations.
Question 2: When should a professional evaluation be sought for the sensation of a “zumbido” in the right ear?
Professional evaluation is recommended if the ringing persists for more than a week, is accompanied by hearing loss, dizziness, or headache, or significantly impacts daily activities.
Question 3: Can stress or anxiety exacerbate the perception of tinnitus in the right ear?
Stress and anxiety can amplify the perceived intensity of tinnitus. Techniques for stress management may provide some relief. Psychological factors, when combined with physiological stimuli, can heighten the aural perception.
Question 4: Is there a definitive cure for tinnitus affecting only the right ear?
A singular cure is not universally available. Treatment focuses on managing symptoms and addressing underlying causes. Sound therapy, hearing aids, and cognitive behavioral therapy may be recommended.
Question 5: How is hearing loss in the right ear related to the sensation of ringing?
Hearing loss, often associated with damage to the auditory nerve or inner ear structures, can disrupt normal auditory processing, leading to the perception of phantom sounds. The sensation is the brain’s interpretation of irregular or absent sound signals.
Question 6: What diagnostic tests are typically performed to evaluate ringing in the right ear?
Common tests include audiometry to assess hearing function, tympanometry to evaluate middle ear function, and imaging studies (MRI or CT scan) to rule out structural abnormalities. These assessments are aimed at identifying and isolating the underlying etiology of the subjective sound.
These answers provide a foundational understanding of the auditory experience, emphasizing the importance of professional evaluation for persistent or concerning symptoms.
The following section will summarize key concepts and provide concluding remarks.
Conclusion
The exploration of “porque me zumba el oido derecho que significa” reveals a complex interplay of potential causes, ranging from benign conditions to more serious underlying pathologies. Understanding that this phrase represents a subjective auditory experience necessitates a thorough and systematic approach to diagnosis and management. Key aspects such as symptom duration, laterality, and individual impact significantly influence the investigative pathway. Moreover, factors ranging from simple cerumen impaction to neurological disorders must be considered when evaluating unilateral auditory phenomena. The multi-faceted nature of the issue demands a comprehensive evaluation to ensure an accurate diagnosis.
Given the potential for persistent or debilitating effects arising from the perception of sounds within the right ear, proactive investigation is crucial. While the source of “porque me zumba el oido derecho que significa” may often be treatable, early intervention offers the best opportunity to alleviate the symptom and prevent further auditory or psychological complications. Continued research and improved diagnostic techniques hold promise for more targeted and effective treatments in the future. Individuals experiencing this symptom should seek professional audiological evaluation to determine the etiology and to implement appropriate management strategies, as timely intervention can significantly improve outcomes.