The sensation of ringing, buzzing, or hissing in the left ear, experienced without an external source, is a phenomenon often interpreted within cultural beliefs as holding specific significance. This subjective auditory perception, frequently described as “tinnitus” in medical terms, can vary in intensity and pitch, ranging from a faint hum to a piercing shriek.
Throughout history, various cultures have attributed spiritual or superstitious meanings to such occurrences. Some traditions consider ringing in the left ear as a sign of negative gossip or impending misfortune, while others view it as a message from the spiritual realm. The belief stems from ancient folklore and continues to influence interpretations of bodily sensations within certain communities. This persistent cultural relevance highlights the intersection of personal experience and collective belief systems.
While these cultural interpretations remain prevalent, understanding potential medical causes and seeking professional evaluation is essential. This article will explore both the cultural significance and potential physiological explanations for auditory disturbances, providing a balanced perspective on this widespread experience.
Understanding Auditory Sensations
Individuals experiencing an unusual auditory perception in the left ear may find the following information helpful for informed decision-making regarding their health and well-being.
Tip 1: Monitor the Sound’s Characteristics: Pay close attention to the specific qualities of the sound. Is it a ringing, buzzing, hissing, or a combination of these? Note the pitch (high or low), intensity (loud or soft), and whether it is constant or intermittent. These details are crucial for subsequent evaluation.
Tip 2: Identify Triggering Factors: Attempt to identify any potential triggers or situations that exacerbate the auditory perception. Consider factors such as loud noises, stress, caffeine intake, alcohol consumption, certain medications, or changes in altitude. Documenting these associations can provide valuable insights.
Tip 3: Review Current Medications: Some medications are known to have ototoxic effects, meaning they can damage the inner ear and lead to auditory disturbances. Consult with a healthcare professional to review current medications and determine if any are potential contributors to the auditory sensation.
Tip 4: Consider Underlying Health Conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as high blood pressure, cardiovascular disease, temporomandibular joint (TMJ) disorders, and Meniere’s disease, can be associated with auditory perceptions. Discussing these possibilities with a healthcare provider is advisable.
Tip 5: Limit Exposure to Loud Noises: Excessive exposure to loud noises is a common cause of tinnitus and other auditory problems. When exposed to potentially damaging sound levels, wear appropriate hearing protection, such as earplugs or earmuffs.
Tip 6: Manage Stress Levels: Stress and anxiety can exacerbate auditory sensations. Implement stress management techniques, such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, yoga, or regular physical activity, to help mitigate the impact of stress on auditory health.
Tip 7: Seek Professional Evaluation: If the auditory perception persists, worsens, or is accompanied by other symptoms such as hearing loss, dizziness, or vertigo, seek prompt evaluation by a qualified audiologist or otolaryngologist (ENT specialist). Early diagnosis and treatment can improve outcomes.
By carefully observing the characteristics of the auditory sensation, identifying potential triggers, and addressing underlying health factors, individuals can take proactive steps toward managing their auditory health and improving their overall well-being. It is emphasized that this information is not a substitute for professional medical advice.
The next section will explore specific medical conditions that may be related to these auditory sensations.
1. Cultural Interpretations
The experience of auditory sensations in the left ear, often inquired about through the phrase “que significa cuando tu oido izquierdo me zumba,” transcends mere physiological occurrences and enters the realm of cultural interpretation. Various societies throughout history have attributed symbolic meanings to such bodily signals, influencing how individuals perceive and react to them.
- Omen of Gossip or News
In certain cultures, a ringing or buzzing in the left ear is considered an omen related to gossip or the impending arrival of news. Specifically, it may be interpreted as an indication that someone is speaking negatively about the individual experiencing the sensation. The left side is frequently associated with negativity or deception in these belief systems, lending credence to the interpretation. This belief can lead to heightened awareness of social interactions and potential conflicts.
- Message from the Spiritual Realm
Alternatively, some spiritual traditions view the left ear as a conduit for messages from the spiritual realm. A buzzing sound might be interpreted as an attempt by deceased loved ones, spirit guides, or other entities to communicate with the individual. The specific meaning of the message often depends on the context of the individual’s life and current circumstances, requiring introspection and discernment to decipher.
- Sign of Imbalance or Disharmony
In holistic health practices, a persistent auditory sensation in the left ear can be perceived as a sign of an imbalance or disharmony within the body or mind. This perspective aligns with the concept of interconnectedness, where physical symptoms are viewed as manifestations of deeper emotional or spiritual issues. Addressing these underlying imbalances through practices such as meditation, energy work, or lifestyle changes is believed to alleviate the sensation.
- Superstition and Folklore
Superstitions and folklore often provide simple explanations for unexplained phenomena. In this context, left ear buzzing might be attributed to the presence of malevolent spirits or the influence of external forces. These beliefs typically involve prescribed actions or rituals to ward off negative influences and restore balance. While such interpretations may lack scientific basis, they can provide comfort and a sense of control in the face of uncertainty.
The diverse range of cultural interpretations associated with left ear auditory sensations illustrates the subjective and context-dependent nature of these experiences. While modern medicine offers physiological explanations for such phenomena, the enduring presence of cultural beliefs underscores the profound influence of tradition and belief systems on human perception and well-being.
2. Subjective Auditory Perception
The phrase “que significa cuando tu oido izquierdo me zumba” directly relates to subjective auditory perception. This perception involves experiencing sounds, such as buzzing, ringing, or hissing, within the ear without an external stimulus. It is a highly individual experience, influenced by a multitude of factors and subject to varied interpretations.
- Nature of the Sensation
The specific qualities of the perceived sound are central to subjective auditory perception. Individuals may describe the sound as a high-pitched ringing, a low hum, a pulsating tone, or a complex combination of noises. This variability in sound characteristics contributes to the challenge in diagnosing the underlying cause. For instance, a high-frequency ringing might suggest noise-induced hearing damage, while a pulsating sound could indicate a vascular issue. These nuances inform the diagnostic process.
- Individual Variability
Subjective auditory perceptions vary significantly among individuals, even when exposed to similar conditions. Factors such as age, pre-existing hearing conditions, overall health, and emotional state can influence how a person perceives and reacts to these sounds. Two individuals with identical levels of noise exposure might experience vastly different subjective auditory sensations, highlighting the complex interplay between external stimuli and individual physiology.
- Emotional and Psychological Impact
The emotional and psychological impact of subjective auditory perception can be substantial. Persistent or intrusive sounds can lead to anxiety, stress, difficulty concentrating, and sleep disturbances. In some cases, the perceived sounds can significantly affect an individual’s quality of life, leading to depression or social isolation. The psychological burden is often amplified by the lack of a definitive cure, necessitating a comprehensive approach to management that addresses both the physical and emotional aspects.
- Influence of Cognitive Factors
Cognitive factors, such as attention and expectation, can modulate the perception of subjective auditory phenomena. Focusing attention on the perceived sound can amplify its intensity, while diverting attention away from it can reduce its prominence. Similarly, expectations based on cultural beliefs or prior experiences can influence how an individual interprets and reacts to the sound. Cognitive behavioral therapy techniques are often employed to address these cognitive factors and help individuals manage their reactions to the perceived sounds.
These facets of subjective auditory perception underscore its complexity and the challenges associated with understanding the meaning behind “que significa cuando tu oido izquierdo me zumba.” A thorough evaluation requires consideration of the sound’s characteristics, individual factors, emotional impact, and cognitive influences to determine the most appropriate course of action. This approach acknowledges the multifaceted nature of the experience and emphasizes the importance of personalized care.
3. Potential Medical Causes
The question of “que significa cuando tu oido izquierdo me zumba” often leads to a consideration of potential underlying medical conditions. While cultural interpretations exist, physiological factors can contribute to the sensation of buzzing or ringing in the ear. Examining these medical possibilities provides a framework for understanding the phenomenon.
- Tinnitus
Tinnitus, the perception of sound when no external noise is present, is a primary medical explanation. It can arise from various factors, including age-related hearing loss, exposure to loud noises, earwax blockage, or changes in ear bone structure. In the context of “que significa cuando tu oido izquierdo me zumba,” tinnitus suggests a disturbance within the auditory system that requires investigation. For example, prolonged exposure to loud music can damage the hair cells in the inner ear, leading to tinnitus localized in one or both ears.
- Meniere’s Disease
Meniere’s disease is an inner ear disorder that can cause episodes of vertigo, hearing loss, tinnitus, and a feeling of fullness in the ear. When an individual experiencing “que significa cuando tu oido izquierdo me zumba” also reports dizziness or fluctuating hearing, Meniere’s disease becomes a relevant consideration. The symptoms typically affect one ear initially, aligning with the unilateral nature of the auditory sensation.
- Acoustic Neuroma
Acoustic neuroma, a noncancerous tumor on the vestibulocochlear nerve leading from the inner ear to the brain, can manifest as tinnitus, hearing loss, and balance problems. Although less common, it is a significant differential diagnosis when investigating “que significa cuando tu oido izquierdo me zumba.” The tumor’s growth can compress the nerve, disrupting auditory signals and causing unilateral symptoms.
- Cardiovascular Issues
Certain cardiovascular conditions, such as high blood pressure or atherosclerosis, can affect blood flow to the inner ear and contribute to pulsatile tinnitus, a type of tinnitus that sounds like a heartbeat. If “que significa cuando tu oido izquierdo me zumba” is described as rhythmic or pulsating, vascular abnormalities should be evaluated. Reduced blood flow to the cochlea can damage sensory cells, leading to auditory disturbances.
These medical causes offer a starting point for investigating the physiological basis of “que significa cuando tu oido izquierdo me zumba.” It is important to consult with a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and management, as the underlying cause may require specific interventions.
4. Neurological Connection
The perception of auditory sensations, particularly when inquiring about “que significa cuando tu oido izquierdo me zumba,” is intrinsically linked to neurological pathways and brain function. The auditory system’s complexity extends beyond the ear itself, involving intricate neural networks that process and interpret sound. Dysfunction or aberrant activity within these networks can manifest as phantom sounds, emphasizing the pivotal role of neurological connections in understanding such experiences. Damage to the auditory nerve, for instance, can disrupt the normal flow of signals to the brain, resulting in misinterpretations or the generation of spurious auditory percepts. This highlights that even when the ear is structurally sound, neurological issues can be the source of the perceived buzzing or ringing.
Further illustrating this connection, conditions like multiple sclerosis, which affects the central nervous system, can sometimes present with auditory symptoms, including tinnitus. The demyelination process associated with multiple sclerosis can disrupt the transmission of nerve impulses, leading to a variety of neurological manifestations, some of which involve auditory pathways. Similarly, traumatic brain injuries can damage auditory processing centers in the brain, resulting in altered auditory perception. These examples underscore the potential for neurological disorders to directly impact auditory experiences and contribute to the phenomenon described by “que significa cuando tu oido izquierdo me zumba.” Diagnostic investigations often incorporate neurological assessments to rule out or identify these underlying conditions, informing treatment strategies.
In summary, the neurological connection forms a crucial component in understanding the subjective experience of auditory sensations. Neurological factors can initiate, modulate, or exacerbate auditory phenomena. A comprehensive evaluation of “que significa cuando tu oido izquierdo me zumba” necessitates considering the intricate interplay between the auditory system and the brain, enabling accurate diagnosis and targeted management strategies. While cultural beliefs may influence interpretation, the underlying physiological mechanisms often have a neurological basis.
5. Auditory System Function
Auditory system function is fundamentally linked to the experience described by “que significa cuando tu oido izquierdo me zumba.” The integrity and proper operation of the auditory system, from the outer ear to the auditory cortex, are essential for accurate sound perception. Disruptions at any point along this pathway can lead to the perception of phantom sounds, such as buzzing or ringing, even in the absence of external stimuli.
- Outer Ear and Sound Collection
The outer ear, including the pinna and ear canal, is responsible for collecting sound waves and channeling them towards the eardrum. Blockages in the ear canal, such as excessive earwax, can alter the way sound is conducted, leading to abnormal pressure on the eardrum. This altered pressure can manifest as a buzzing sensation in the ear, directly relating to “que significa cuando tu oido izquierdo me zumba.” For example, impacted cerumen can create a low-frequency buzzing sound, particularly noticeable in quiet environments.
- Middle Ear and Sound Amplification
The middle ear contains three small bones (malleus, incus, and stapes) that amplify sound vibrations and transmit them to the inner ear. Conditions affecting these bones, such as otosclerosis (abnormal bone growth), can impair sound transmission and result in tinnitus or other auditory distortions. In cases related to “que significa cuando tu oido izquierdo me zumba,” otosclerosis affecting the left ear could lead to a perceived buzzing sound due to inefficient vibration transfer. This highlights the mechanical importance of the middle ear in accurate sound perception.
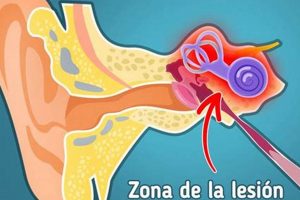
- Inner Ear and Sensory Transduction
The inner ear houses the cochlea, which contains sensory hair cells that convert sound vibrations into electrical signals that are sent to the brain. Damage to these hair cells, often caused by loud noise exposure or age-related degeneration, is a common cause of tinnitus. The specific frequency of the perceived tinnitus often corresponds to the region of the cochlea that is most affected. In instances of “que significa cuando tu oido izquierdo me zumba,” damage to hair cells in the left cochlea could result in a high-pitched ringing or buzzing sound. This is because the hair cells transduce mechanical energy into neural signals for auditory processing, and damage disrupts this process.
- Auditory Nerve and Brain Processing
The auditory nerve transmits electrical signals from the cochlea to the brainstem and auditory cortex, where sound is processed and interpreted. Lesions or abnormalities along this neural pathway can disrupt the accurate transmission of auditory information, leading to aberrant sound perception. In the context of “que significa cuando tu oido izquierdo me zumba,” a tumor pressing on the auditory nerve or a demyelinating condition affecting the nerve fibers could generate a buzzing sensation in the left ear. The brain’s interpretation of these distorted signals results in the subjective experience of phantom sounds.
These aspects of auditory system function illustrate how disruptions at various stages of the auditory pathway can contribute to the sensation described by “que significa cuando tu oido izquierdo me zumba.” A comprehensive understanding of these mechanisms is crucial for accurate diagnosis and appropriate management of auditory symptoms, as they connect to the inner workings of the ear in hearing process.
Frequently Asked Questions
The following questions address common inquiries regarding the experience of auditory sensations, specifically the perception of buzzing or ringing in the left ear.
Question 1: Are auditory sensations in the left ear always indicative of a serious medical condition?
Not necessarily. While persistent or concerning auditory sensations warrant medical evaluation, transient occurrences may be benign and related to temporary factors such as stress, noise exposure, or mild earwax accumulation. However, it is crucial to differentiate between transient and persistent symptoms to determine the need for further investigation.
Question 2: Can cultural beliefs influence the perception or interpretation of auditory sensations?
Yes, cultural beliefs can significantly influence the perception and interpretation of auditory sensations. Certain cultures attribute symbolic meanings to ringing or buzzing in the ears, often associating it with gossip, spiritual messages, or omens. These beliefs can shape an individual’s emotional response to the sensation and their willingness to seek medical attention.
Question 3: What are the initial steps to take when experiencing persistent auditory sensations in the left ear?
The initial steps involve documenting the characteristics of the sensation (e.g., pitch, intensity, and duration), identifying potential triggers, and reviewing current medications. Maintaining a log of these factors can provide valuable information for a healthcare professional during evaluation. Limiting exposure to loud noises and managing stress levels are also recommended.
Question 4: Which medical professionals are best suited to evaluate auditory sensations in the ear?
An audiologist or otolaryngologist (ENT specialist) is best suited to evaluate auditory sensations. An audiologist can perform hearing tests and assess the function of the auditory system, while an otolaryngologist can examine the ear, nose, and throat to identify potential underlying medical conditions.
Question 5: Are there any over-the-counter remedies or self-treatments that can alleviate auditory sensations in the ear?
While some over-the-counter products claim to alleviate tinnitus or other auditory sensations, their effectiveness is not consistently supported by scientific evidence. Self-treatments such as earwax removal kits may be helpful in certain cases, but it is crucial to exercise caution and avoid causing injury to the ear. It is recommended to consult with a healthcare professional before using any self-treatment methods.
Question 6: What are some potential long-term consequences of ignoring persistent auditory sensations in the ear?
Ignoring persistent auditory sensations can lead to several potential long-term consequences, including chronic tinnitus, hearing loss, sleep disturbances, anxiety, and depression. In some cases, the underlying cause of the auditory sensation may be a serious medical condition that requires prompt treatment to prevent further complications. Early diagnosis and management are crucial for mitigating these risks.
The experience of auditory sensations in the ear is complex and multifactorial. Understanding the potential causes, seeking timely medical evaluation, and adopting appropriate management strategies are essential for maintaining auditory health and overall well-being.
The following section will explore management and treatment options for dealing with such auditory symptoms.
Understanding Auditory Sensations
This exploration of “que significa cuando tu oido izquierdo me zumba” has illuminated the multi-faceted nature of this experience, spanning from cultural interpretations to potential medical etiologies. The investigation has considered subjective auditory perception, neurological underpinnings, and the function of the auditory system. Emphasis has been placed on the importance of differentiating cultural beliefs from verifiable medical conditions, and it has underscored the necessity of seeking professional medical evaluation when symptoms persist or worsen. The variety of conditions, from tinnitus to Meniere’s disease, highlights the necessity for careful diagnosis.
Given the potential for auditory sensations to indicate underlying health issues, persistent symptoms require prompt attention. A comprehensive understanding of personal experiences, coupled with professional guidance, supports informed decision-making. Prioritizing auditory health contributes to overall well-being, fostering improved quality of life and minimizing the potential for long-term complications. Seeking clarity through medical consultation offers a pathway toward understanding and managing auditory experiences effectively.