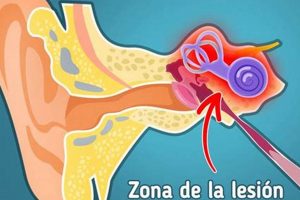
The sensation of ringing, buzzing, or hissing in the ears, often described as “zumba el oido,” refers to tinnitus. This auditory perception occurs in the absence of an external sound source. Individuals may experience it intermittently or continuously, and the perceived sound can vary in pitch and intensity.
Understanding the underlying causes and potential management strategies for this condition is crucial for improving quality of life. Tinnitus can negatively impact concentration, sleep, and emotional well-being. Historically, remedies have ranged from folk medicine to advanced medical interventions, reflecting the persistent search for effective solutions. Current understanding emphasizes addressing contributing factors and implementing coping mechanisms.
Addressing this aural phenomenon involves identifying potential triggers, exploring available medical treatments, and implementing self-management techniques. Further discussion will delve into specific diagnostic procedures, therapeutic options, and lifestyle adjustments that can help mitigate the effects of this condition.
Management Strategies for Tinnitus
Individuals experiencing persistent ringing in the ears can employ various strategies to manage the condition and minimize its impact on daily life. The following tips outline evidence-based approaches and lifestyle adjustments that may offer relief.
Tip 1: Seek Professional Evaluation: An audiologist or physician can conduct a thorough hearing assessment to identify potential underlying causes, such as hearing loss or medical conditions. Early diagnosis is crucial for effective management.
Tip 2: Manage Stress Levels: Stress can exacerbate tinnitus symptoms. Techniques such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, and yoga can help reduce stress and alleviate the perceived intensity of the ringing.
Tip 3: Protect Hearing: Exposure to loud noise is a common trigger for tinnitus. Using earplugs or earmuffs in noisy environments can prevent further damage to the auditory system and reduce the risk of symptom aggravation.
Tip 4: Limit Caffeine and Alcohol Consumption: These substances can affect blood flow and nervous system activity, potentially worsening tinnitus symptoms. Monitoring intake and adjusting consumption habits may provide relief.
Tip 5: Utilize Sound Therapy: Introducing background noise, such as white noise or nature sounds, can mask the tinnitus sound and make it less noticeable. Sound generators or ambient sound apps can be valuable tools.
Tip 6: Consider Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): CBT can help individuals develop coping strategies for managing the emotional distress associated with tinnitus. A therapist can provide guidance on modifying negative thought patterns and behaviors related to the condition.
These strategies, when implemented consistently, can contribute to improved management of tinnitus and a better quality of life. It is important to remember that individual responses may vary, and consulting with healthcare professionals is essential for personalized guidance.
The subsequent sections will address further considerations, including potential medical interventions and long-term management approaches.
1. Identify potential cause.
Determining the potential cause of the auditory sensation, often described as “que hacer cuando zumba el oido,” forms the cornerstone of effective management. The presence of this symptom can originate from a variety of sources, each requiring a specific approach to diagnosis and treatment. Identifying the root cause enables tailored interventions, optimizing the likelihood of symptom reduction and improved quality of life.
- Noise-Induced Hearing Loss
Prolonged exposure to loud noises, either occupational or recreational, is a frequent trigger. The damage to hair cells within the inner ear can manifest as tinnitus. Identifying this etiology necessitates a detailed history of noise exposure and audiometric testing to assess the degree of hearing loss. Management focuses on hearing protection and potentially sound therapy.
- Medical Conditions
Certain medical conditions, such as Meniere’s disease, otosclerosis, and temporomandibular joint (TMJ) disorders, can contribute to tinnitus. Diagnosing these conditions involves thorough medical examination and specific diagnostic tests. Treatment addresses the underlying medical issue, which may subsequently alleviate the aural symptom.
- Medications
Numerous medications, including certain antibiotics, anti-inflammatory drugs, and antidepressants, have been associated with tinnitus as a side effect. A review of the individual’s medication list is crucial. If a medication is suspected, discontinuation or substitution, under medical supervision, may be considered to assess its contribution.
- Stress and Psychological Factors
Stress, anxiety, and depression can exacerbate or even trigger tinnitus in some individuals. Addressing these psychological factors through therapies like cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) or stress management techniques can significantly improve coping mechanisms and perceived symptom intensity.
Establishing the underlying cause of “que hacer cuando zumba el oido” is an iterative process. It often requires collaboration between the patient, audiologist, and physician to gather a comprehensive medical history, perform appropriate diagnostic testing, and interpret the results accurately. This thoroughness ensures that the most appropriate and effective management strategies are implemented.
2. Medical consultation essential.
Addressing the symptom described as “que hacer cuando zumba el oido” mandates a prompt and thorough medical consultation. This step transcends mere symptom management; it represents a critical juncture in identifying potentially serious underlying conditions and initiating appropriate interventions. Delaying consultation can lead to delayed diagnosis and potentially compromise treatment outcomes.
- Differential Diagnosis
A medical professional can conduct a differential diagnosis, distinguishing tinnitus from other conditions presenting with similar symptoms. This process involves ruling out potential causes such as vascular abnormalities, neurological disorders, or medication side effects. Accurate diagnosis necessitates specialized expertise and diagnostic tools unavailable outside a clinical setting. Failing to consult a medical professional can lead to misdiagnosis and inappropriate treatment.
- Assessment of Hearing Function
Audiological evaluation is integral to assessing the overall hearing function. This assessment helps determine the presence and degree of any underlying hearing loss, a common correlate of tinnitus. Identifying hearing loss is essential for developing appropriate management strategies, which may include hearing aids or other assistive devices. Without proper evaluation, the impact of hearing loss on the tinnitus experience may be overlooked.
- Identification of Treatable Medical Conditions
In some instances, tinnitus can be a symptom of an underlying treatable medical condition, such as otosclerosis, Meniere’s disease, or thyroid disorders. Medical consultation facilitates the identification of these conditions, enabling targeted treatment that can alleviate the tinnitus. Delaying consultation may allow these underlying conditions to progress, potentially complicating treatment and increasing the risk of irreversible damage.
- Development of a Comprehensive Management Plan
A medical professional can develop a personalized management plan that addresses the specific needs and circumstances of the individual experiencing “que hacer cuando zumba el oido.” This plan may incorporate a combination of medical treatments, sound therapy, counseling, and lifestyle modifications. A comprehensive and individualized approach is essential for maximizing the effectiveness of tinnitus management.
The multifaceted benefits of seeking professional medical advice when experiencing the auditory phenomenon underscore the critical nature of this step. It not only aids in addressing the symptom itself but also plays a pivotal role in safeguarding overall health and well-being. Prompt consultation is therefore not merely recommended, but an essential component in the effective management of “que hacer cuando zumba el oido.”
3. Hearing protection paramount.
The imperative of hearing protection arises significantly in the context of “que hacer cuando zumba el oido.” Preventing auditory damage is more effective than treating its consequences. Consistent and appropriate hearing protection strategies are essential to mitigate the risk of developing or exacerbating this aural sensation.
- Primary Prevention of Auditory Trauma
Hearing protection serves as a primary preventative measure against noise-induced hearing loss, a leading cause of tinnitus. Individuals exposed to high noise levels in occupational or recreational settings are particularly vulnerable. The use of earplugs or earmuffs reduces the intensity of sound reaching the inner ear, minimizing the risk of damage to the delicate hair cells responsible for auditory transduction. Consistent application of hearing protection during activities like concerts, construction work, or shooting sports can substantially decrease the likelihood of developing tinnitus.
- Mitigation of Existing Tinnitus Symptoms
For individuals already experiencing tinnitus, hearing protection remains crucial. Exposure to loud sounds can exacerbate existing tinnitus symptoms, increasing the perceived loudness and distress associated with the condition. By minimizing additional auditory trauma, individuals can help prevent the worsening of their tinnitus. This strategy is particularly relevant in environments where noise levels fluctuate unpredictably.
- Selection of Appropriate Protective Devices
The effectiveness of hearing protection depends on the selection of appropriate devices. Earplugs are typically suitable for moderate noise levels, while earmuffs provide greater attenuation in louder environments. Custom-molded earplugs offer a personalized fit and enhanced comfort, making them ideal for prolonged use. It is important to choose devices that provide adequate noise reduction without compromising the ability to hear essential sounds, such as speech or warning signals.
- Education and Awareness Programs
Promoting hearing protection requires education and awareness programs targeted at individuals at risk. These programs should emphasize the importance of consistent use, proper fit, and the potential long-term consequences of noise exposure. Employers have a responsibility to provide adequate hearing protection and training to their employees working in noisy environments. Public health campaigns can also raise awareness about the importance of protecting hearing during recreational activities.
The comprehensive implementation of hearing protection strategies, encompassing preventative measures, symptom mitigation, appropriate device selection, and educational initiatives, represents a cornerstone in addressing “que hacer cuando zumba el oido.” Prioritizing hearing conservation contributes significantly to preserving auditory health and minimizing the burden of this pervasive aural sensation.
4. Stress reduction techniques.
The interplay between stress and the perception of “que hacer cuando zumba el oido” necessitates the incorporation of effective stress reduction techniques into management strategies. Elevated stress levels can exacerbate tinnitus symptoms, creating a feedback loop where the aural sensation intensifies perceived stress, and vice versa. Addressing stress, therefore, becomes a critical component in alleviating the impact of tinnitus on an individual’s quality of life.
- Mindfulness Meditation and Relaxation Exercises
Mindfulness meditation involves focusing on the present moment without judgment, which can help individuals detach from intrusive thoughts and sensations, including the sound associated with tinnitus. Regular practice of relaxation exercises, such as deep breathing or progressive muscle relaxation, can lower physiological arousal and reduce overall stress levels. These techniques empower individuals to manage their response to tinnitus, diminishing its perceived intensity and emotional impact. For instance, a person experiencing increased ringing during periods of high stress could use a guided meditation app to regain a sense of calm and control.
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
CBT is a structured therapeutic approach that helps individuals identify and modify negative thought patterns and behaviors related to tinnitus. By challenging maladaptive beliefs about the condition, individuals can reduce anxiety and improve coping skills. CBT interventions often include relaxation techniques, cognitive restructuring, and exposure therapy to gradually desensitize individuals to the tinnitus sound. Studies have demonstrated that CBT can significantly reduce the distress and functional impairment associated with tinnitus, enabling individuals to lead more fulfilling lives.
- Physical Exercise and Activity
Regular physical activity is a potent stress reliever and can improve overall well-being. Exercise releases endorphins, which have mood-boosting effects, and can help reduce muscle tension and anxiety. Engaging in activities such as walking, swimming, or yoga can provide a distraction from tinnitus and promote a sense of relaxation. Moreover, physical activity can improve sleep quality, further contributing to stress reduction and overall health. A consistent exercise routine can serve as a buffer against the negative impact of stress on tinnitus symptoms.
- Lifestyle Modifications and Time Management
Implementing lifestyle modifications to reduce sources of chronic stress is essential. This may involve improving time management skills, setting realistic goals, and learning to delegate tasks. Prioritizing self-care activities, such as spending time with loved ones or pursuing hobbies, can also enhance resilience to stress. Identifying and eliminating sources of environmental stress, such as excessive noise or workplace demands, is also crucial. By proactively managing stressors, individuals can minimize the likelihood of tinnitus exacerbation and improve their overall sense of control.
Integration of these stress reduction techniques into a comprehensive management plan for “que hacer cuando zumba el oido” is crucial for achieving optimal outcomes. While these techniques may not eliminate tinnitus entirely, they can significantly reduce its perceived impact and improve an individual’s ability to cope with the condition, leading to a more fulfilling and balanced life. Ongoing self-care and stress management practices should be considered essential components of long-term tinnitus management.
5. Sound therapy options.
Sound therapy offers various approaches to manage the auditory perception described as “que hacer cuando zumba el oido”. These methods aim to reduce the perceived loudness or annoyance of tinnitus by introducing external sounds, retraining the auditory system, or masking the tinnitus sensation. The selection of appropriate sound therapy techniques requires careful consideration of individual needs and preferences.
- Masking Techniques
Masking involves using external sounds to partially or completely cover the tinnitus sound. This can be achieved through white noise generators, tinnitus maskers (devices resembling hearing aids that produce a masking sound), or ambient sounds such as nature sounds or music. While masking can provide immediate relief, it does not address the underlying cause of tinnitus and may not be effective for all individuals. Its primary role is to offer temporary respite from the perceived annoyance. An example includes playing a fan at night to mask the tinnitus sound, enabling easier sleep.
- Tinnitus Retraining Therapy (TRT)
TRT is a more comprehensive approach that combines sound therapy with counseling. The goal of TRT is to habituate the individual to the tinnitus sound, reducing its perceived loudness and emotional impact. Sound therapy in TRT typically involves using broadband noise generators at a low level, below the masking threshold, to gradually desensitize the auditory system. Counseling helps individuals understand the mechanisms of tinnitus and develop coping strategies. TRT requires a significant commitment from the individual and is typically administered by a trained audiologist or therapist. An example of TRT is wearing white noise generators for several hours daily, combined with regular counseling sessions.
- Sound Enrichment Strategies
Sound enrichment involves introducing pleasant or neutral sounds into the environment to reduce the contrast between silence and the tinnitus sound. This can be achieved through background music, nature sounds, or simply opening a window to hear ambient sounds. The goal is to make the tinnitus less noticeable by providing a more stimulating auditory environment. Sound enrichment is a relatively simple and low-cost approach that can be easily implemented in daily life. Leaving a television or radio playing at a low volume is an example.
- Hearing Aids
For individuals with both tinnitus and hearing loss, hearing aids can be an effective form of sound therapy. By amplifying external sounds, hearing aids can reduce the contrast between the tinnitus and the environment, making the tinnitus less noticeable. Hearing aids can also improve communication abilities and overall quality of life. In some cases, hearing aids may also include built-in tinnitus maskers to provide additional relief. A hearing aid amplifies external sounds so the patient doesn’t focus on internal sound.
The diverse range of sound therapy options allows for personalized management of “que hacer cuando zumba el oido”. It is crucial to consult with an audiologist or other healthcare professional to determine the most appropriate approach based on the individual’s specific needs and circumstances. Sound therapy, while not a cure for tinnitus, can significantly reduce its impact on daily life and improve overall well-being.
6. Lifestyle adjustments beneficial.
Lifestyle modifications can exert a significant influence on the perception and management of “que hacer cuando zumba el oido”. This connection arises from the interplay between various lifestyle factors and auditory system function. These adjustments are considered a supportive, rather than curative, element in addressing the sensation. Their effectiveness varies based on individual circumstances and the underlying cause of the auditory disturbance. Real-world examples include individuals experiencing reduced tinnitus severity after adopting dietary changes or implementing regular exercise routines. The practical significance of understanding this link lies in empowering individuals to proactively manage their symptoms through modifiable lifestyle factors.
Specific areas of lifestyle adjustment with potential benefits include diet, exercise, sleep hygiene, and substance use. Dietary changes such as reducing sodium intake can mitigate fluid retention in the inner ear, potentially lessening tinnitus symptoms. Regular physical exercise can improve blood circulation and reduce stress, both factors implicated in tinnitus exacerbation. Prioritizing consistent sleep patterns and a conducive sleep environment promotes overall well-being and auditory system stability. Limiting or eliminating alcohol, caffeine, and nicotine, all known stimulants, can reduce their influence on nervous system activity and auditory perception. These changes represent practical applications of lifestyle modifications in tinnitus management.
While lifestyle adjustments alone may not resolve “que hacer cuando zumba el oido,” their integration into a comprehensive management plan offers valuable support. The challenge lies in identifying the specific lifestyle factors that are most influential for each individual. A collaborative approach with healthcare professionals, including audiologists and physicians, ensures tailored recommendations. Lifestyle changes are not a substitute for medical evaluation or treatment but rather a complementary strategy that can contribute to improved symptom management and overall well-being. The beneficial impact of these adjustments underscores the holistic nature of addressing “que hacer cuando zumba el oido”.
Frequently Asked Questions Regarding “Que Hacer Cuando Zumba El Oido”
This section addresses common queries and misconceptions associated with the auditory phenomenon described as “que hacer cuando zumba el oido,” providing factual and clinically relevant information.
Question 1: Is “que hacer cuando zumba el oido” always indicative of a serious medical condition?
While tinnitus can be a symptom of underlying medical conditions, it is frequently associated with factors such as noise exposure or age-related hearing loss. A comprehensive medical evaluation is necessary to determine the specific etiology.
Question 2: Can “que hacer cuando zumba el oido” be cured completely?
A definitive cure for tinnitus is not always possible, particularly when associated with irreversible hearing damage. Management strategies focus on reducing symptom severity and improving quality of life.
Question 3: Are there any over-the-counter remedies that can effectively treat “que hacer cuando zumba el oido”?
The efficacy of over-the-counter remedies for tinnitus is generally unsupported by robust scientific evidence. Medical consultation and evidence-based therapies are recommended.
Question 4: What role does stress play in the experience of “que hacer cuando zumba el oido”?
Stress can exacerbate tinnitus symptoms and negatively impact coping mechanisms. Stress management techniques are frequently incorporated into comprehensive tinnitus management plans.
Question 5: Is hearing protection always effective in preventing “que hacer cuando zumba el oido”?
Consistent and appropriate hearing protection can significantly reduce the risk of noise-induced tinnitus. However, tinnitus can arise from other causes, making hearing protection an incomplete preventative measure.
Question 6: When should one seek immediate medical attention for “que hacer cuando zumba el oido”?
Sudden onset of tinnitus, particularly if accompanied by other symptoms such as hearing loss, dizziness, or facial weakness, warrants immediate medical evaluation to rule out potentially serious underlying conditions.
The information presented aims to provide clarity and dispel misconceptions surrounding “que hacer cuando zumba el oido.” It underscores the importance of professional evaluation and evidence-based management approaches.
Further exploration will focus on specific therapeutic interventions available for managing this auditory phenomenon.
Conclusion
The preceding discussion has provided a comprehensive overview of “que hacer cuando zumba el oido,” encompassing its definition, potential causes, management strategies, and frequently asked questions. Understanding the multifaceted nature of this auditory phenomenon is crucial for individuals experiencing these sensations, enabling informed decision-making and proactive engagement in their care.
Effective navigation of “que hacer cuando zumba el oido” necessitates a collaborative approach involving medical professionals and the implementation of evidence-based interventions. Recognizing the potential impact on quality of life underscores the importance of early diagnosis, appropriate management, and ongoing support to mitigate the effects of this pervasive condition.